The situation of the country in relation to neighboring countries. Economic and geographic situation of countries
The situation of the country in relation to neighboring countriesoften referred to as the economic-geographical position. This is a rather complex and multifaceted category. About her and will be discussed in this article. What are the characteristics of the economic and geographical situation of the leading states of Eurasia - Japan, Britain, France? And how much is it profitable?
The situation of the country in relation to neighboring countries
The countries of our planet differ significantlyfrom friend. And not only in terms of size, population or cultural characteristics. There are other factors that largely determine the welfare of the state. Thus, some countries have an extensive outlet to the ocean, while others are enclosed within the continent. Some states are at the intersection of important transcontinental transport routes, which gives them huge benefits in the form of profit from the transit of goods by other subjects of the world economy. All these factors can be attributed to the concept considered in this article.
So, the situation of the country in relation to neighboringcountries are called the economic and geographical position of the state (abbreviated - EGP). However, this is a very narrow interpretation of the concept. EGP is a very complex and multifaceted geographical category. In a broad sense, EGP is the position of a country (and also of a city or region) relative to those geographical objects that can have an influence (positive or negative) on its economic development.

EGP can be central, peripheral, deep or marginal. It can be assessed at the global or regional level.
When characterizing the EGP of a particular state, many factors should be taken into account. It:
- availability of access to the sea (oceans);
- number of neighboring countries;
- marketing opportunities for their products;
- availability of large fuel and raw materials bases;
- position regarding important transport routes, etc.
It is interesting that some countries successfully usebenefits of its geographical location. Other states have not yet learned this art. Soviet scientist-geographer Nikolai Baransky was the first who seriously dealt with theoretical aspects of the concept of EGP.
Position in relation to neighboring countries is oftenalso called geopolitical position. However, in this case we are talking only about political factors, the nature of the relations of a particular state with its neighbors, and the like.
Characteristics of the EGP of France
France is one of the largest countries in Europe. It includes Corsica, as well as a number of small islands in the Mediterranean Sea. In addition, France owns overseas departments and territories around the world.
The situation of France in relation to neighboring countries can be described as beneficial. It borders on eight states. With each of them, France maintains good-neighborly and close relations.
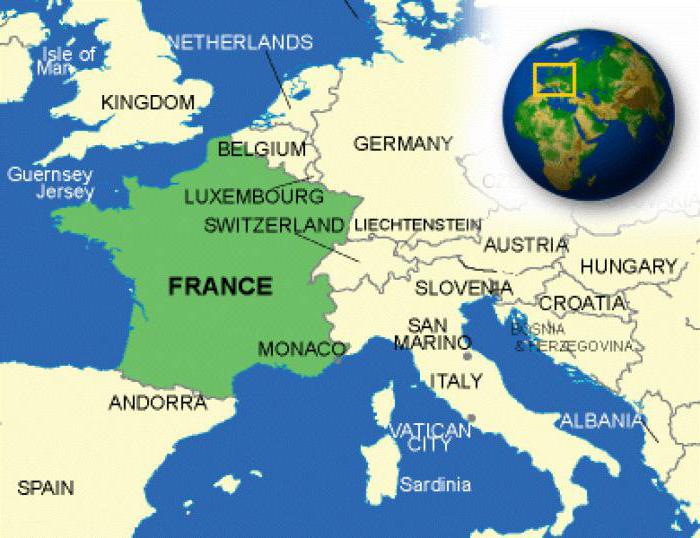
The country is located in Western Europe and hasaccess to the Mediterranean Sea in the south and to the Atlantic in the west and north-west. The coastline within the state is riddled with numerous bays suitable for entering large international vessels.
Characteristics of the EGP of Japan
Japan is an archipelagic country in East Asia,which consists of six thousand islands of various sizes. From the east the territory of the state is washed by the Pacific Ocean, from the west by the waters of the three seas that separate it from the "Big Land".

Japan is frankly unlucky with naturalresources and relief. About 80% of its territory is not suitable for the development of the economy and the construction of residential buildings (due to mountain landscapes). In addition, there are practically no minerals in the country.
Evaluation of UKE
The geographical position of Great Britain in many respects resembles the EHP of Japan. This country is also located on a group of islands, but not on the eastern, but on the western outskirts of Eurasia.
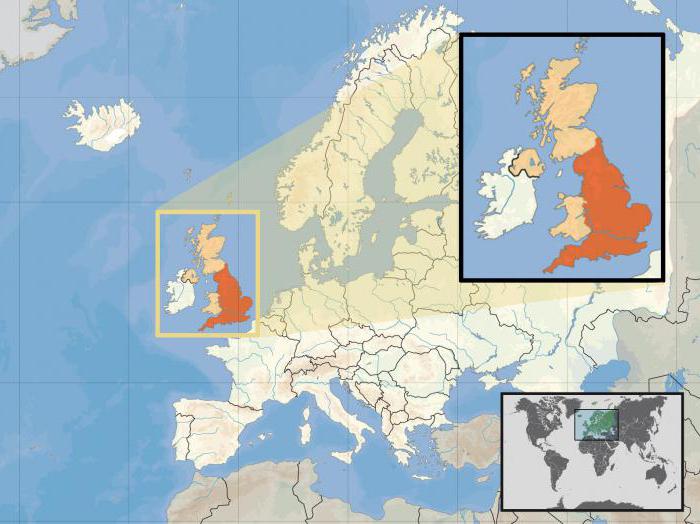
Great Britain is washed by the waters of the Atlantic and twoseas - Northern and Irish. From the mainland it is separated by a 35-kilometer Strait of the English Channel. The common land border has only one country - Ireland.
Due to its geographical location, Englanda few centuries ago received the unspoken status of the "sea queen of Europe." The relief and natural and climatic conditions also contribute to the development of the country's economy.
Conclusion
The term EGP is understood as the country's position onin relation to neighboring countries. It can be central, deep or marginal, profitable or unprofitable. In addition, not all states effectively use their geographical location.
</ p>




