Compound Reaction: Examples and Formula
The reaction of exchange, substitution, compound, decomposition is considered in the course of the school program. Let us analyze the features of each type, give examples of interactions.
Definition of term
What is the reaction of the compound,examples of which are considered in the general educational institutions at the first stage of training? To begin with, we note that the term "chemical reaction" in chemistry is considered the second most important.
In our world, the reaction of a compound takes place every minute, the equations of which are familiar to us, but we do not even think about them.
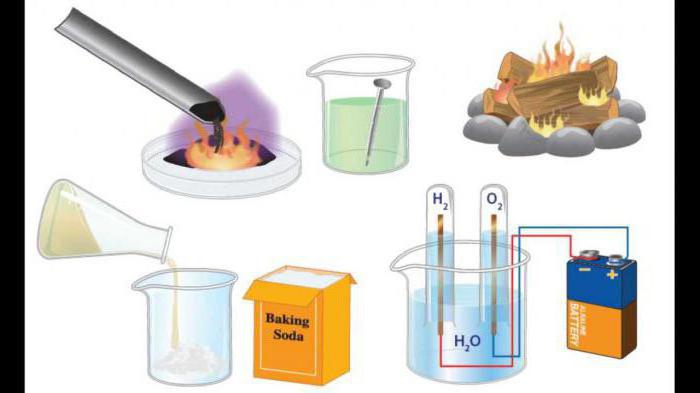
For example, the production of carbonated beverages, the burning of firewood are typical examples of compound reactions.
This process involves obtaining products with a certain qualitative and quantitative composition from the original chemicals.

Signs of chemical reactions
Any process, including the chemical reaction of the compound, is accompanied by certain signs:
- the release of light or heat;
- change in color of solution;
- release of a gaseous substance;
- the appearance of a specific odor;
- dissolution or precipitation.

Reaction conditions
Depending on the characteristics of the qualitative and quantitative composition, the chemical reaction of the compound can proceed under different conditions.
For example, an interaction of the form 2Ca + O2 = 2CaO (quenching of lime) flows without preheating, accompanied by the release of a significant amount of thermal energy.
How is the reaction of the compound formed correctly? The equations of such processes assume the writing of the initial substances on the left side, and the product of the reaction is compiled on the right-hand side.
4Na + O2 = 2Na2O
Such processes are inherent in organic substances. Thus, a qualitative reaction to the uncertainty (the presence of a multiple bond) is the reaction of oxidation of the starting material with potassium permanganate.

Combustion of firewood
This process proceeds according to the equation:
C + O2 = CO2
This is a typical reaction of a compound, examples of whichhave already been cited above. What is the essence of this process? When the firewood interacts with oxygen in the air, carbon dioxide molecules are formed. The process is accompanied by the formation of a new molecule of a compound bond, is an exothermic reaction.
Is it possible between the complex substances reactionconnections? Examples of interactions with simple substances have been discussed above, but this type is also characteristic of complex substances. A typical variant of such interaction is the reaction of lime quenching.
CaO + H2O = Ca (OH)2
This process is also accompanied by the release of a significant amount of thermal energy. Among the specific features of this process, we note its spontaneity.
Classification
The composition of the initial substances and reaction products releases the reaction of the compound, decomposition, substitution, exchange. Let us consider their examples, and also give definitions of such processes.
Substitution is the substitution of a part of a compound by the atoms of a simple substance.
Joining is the process of combining several simple or complex substances into one more complex one. Examples of such processes can be derived from inorganic and organic chemistry.
2H2 + O2 = 2H2 O
This process occurs with the release of a significant amount of heat, so an explosion is possible.
C2 H4 + H2 = C2 H6
When hydrogen is passed through ethylene, a double bond breaks up, the formation of a saturated hydrocarbon is formed.
Decomposition - these are the chemical reactions that result in the formation of several substances from one complex compound, having a simpler qualitative and quantitative composition.
Ion exchange reactionsa are processes occurring between complex substances, as a result of which an exchange of components takes place.
There are three conditions for the flow of such a process: the evolution of gas, the precipitation of sediment, the formation of a poorly dissociated substance.
This interaction is called esterification, soas the final product of the reaction is an ester. The condition of the process in the forward direction is the introduction of concentrated sulfuric acid into the reaction mixture.

Division by aggregate state of interacting substances
All chemical processes are classified according to thisa sign of homogeneous and heterogeneous interactions. In the first case, the initial substances and the reaction products are in the same aggregate state, and for heterogeneous species a different state is allowed.
For example, the following interaction will be a homogeneous process:
H2(gas) + Cl2(gas) = 2HCl (gas)
The following variant can be considered as a heterogeneous reaction:
CaO (s) + H2O (g) = Ca (OH)2 (p-p)

By changing the degree of oxidation
The reaction of the compound, the formula of which wasis given above (the formation of water from simple substances), is an oxidation-reduction process. The essence of the process lies in the fact that the acceptance and release of electrons takes place.
Among the reactions of the compound, there are also such processes that are not accompanied by a change in the degrees of oxidation, that is, they are not OVR:
CaO + H2O = Ca (OH)2
By the nature of leakage
Depending on whether the process can proceed only in the forward direction or the reaction occurs in the opposite direction, irreversible and reversible interactions are distinguished in chemistry.
For example, a qualitative response to organiccompound is irreversible, since it leads to the formation of an insoluble or gaseous substance. An example of such a qualitative interaction is the reaction of the "silver mirror", which is a qualitative method of determination in a mixture of aldehydes.
Among the typical variants of reversible reactions that are capable of flowing in two mutually opposite directions, we note the esterification reaction:
CO2 + H2O = H2CO3
On the use of catalyst
In some cases, it is necessary to use an accelerator (catalyst) in order for the chemical process to proceed. An example of catalytic interaction is the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide.

Features of IRS parsing
Among the issues that most often causedifficulties for schoolchildren, is the arrangement of coefficients in the reaction using the electronic balance method. To begin with, there are certain rules according to which in each substance it is possible to determine the oxidation states of individual elements.
Regardless of whether a simple or complex substance will be considered, the sum of them must be zero.
The next stage will be the choice of those substances orseparate chemical elements, in which the value of oxidation degree has changed. They write out separately, showing the signs of "plus" or "minus" the number of received or given electrons.
Between these digits, the smallest number is found, when divided by the number of received and given electrons, integers will be obtained.
The numbers obtained are stereochemicalcoefficients, arranged in the equation of the proposed process. An important stage in the analysis of oxidation-reduction reactions is the determination of the oxidizing agent and reducing agent, as well as the recording of the processes occurring. As the reducing agent, those atoms or ions are chosen which, during the course of the interaction, increased their oxidation state, for the oxidizer, on the contrary, a decrease in this index is characteristic.
Does this algorithm assume anyorganic chemistry? The reaction of a compound, substitution, decomposition, flow with a change in oxidation states is considered by a similar algorithm.
There are certain peculiarities in the arrangement of degrees of oxidation in organic compounds, but their sum should also be zero.
Depending on how the degree of oxidation changes, several types of chemical interactions are distinguished:
- disproportionation - is associated with a change in the degrees of oxidation of one and the same element to a greater or lesser extent;
- counterproportionation - involves the interaction of a reducing agent and an oxidizer, which contain the same element, but in different degrees of oxidation.
Conclusion
As a small summary, we note that wheninteraction of substances with each other are their changes, transformations. Chemical reactions are the transformation of one or several reagents into products having a different qualitative and quantitative composition.
If a change is observed in nuclear transformationsthe composition of the atomic nuclei, then in the case of chemical reactions this is not the case, only redistribution of nuclei and electrons occurs, leading to the appearance of new compounds.
Occurring processes can be accompanied by the release of light, heat, the appearance of odor, precipitation, the formation of gaseous substances.
There are many variants of classificationorganic and inorganic interactions on different grounds. Among the most common variants we can mention the change in oxidation states, the aggregate state, the reversibility of the flow, the mechanism of the process, the use of a catalyst (inhibitor).
Chemical reactions are the basis not only of industrial production, but also the basis of life. Without metabolic processes that take place in living organisms, existence would be impossible.
</ p>


