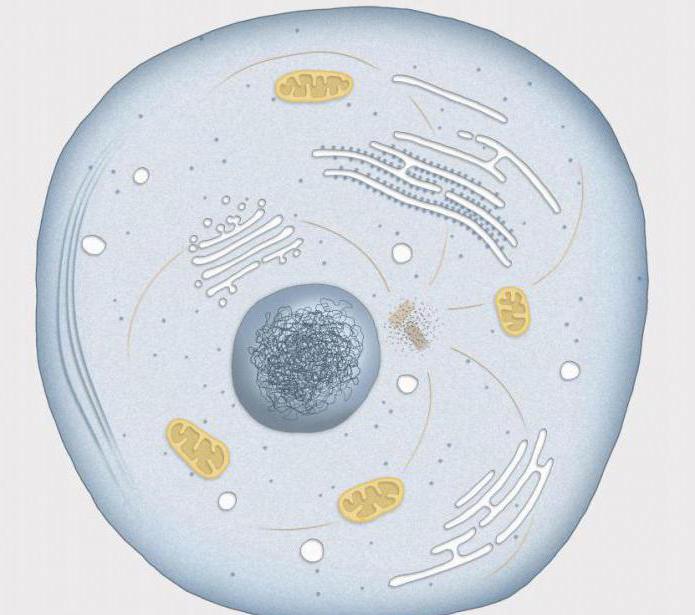
What is mitosis and what is the process in the prophase of mitosis?
What is mitosis and meiosis and what phases do they have? This division of cells, which has some differences. With meiosis, four daughter cells are formed from the mother nucleus, in which the number of chromosomes is decreased (twice). With mitosis, cell division also occurs, but only two daughter cells with the same chromosomes are formed as in the case of parents.

So what is mitosis and meiosis? These are biological fission procedures, during which cells with certain chromosomes are formed. Reproduction by mitosis occurs in multicellular, complex living organisms.
Stages of
Mitosis proceeds in two stages:
- Doubling of information at the gene level. Here, the mother cells distribute genetic information among themselves. At this stage, the chromosomes change.
- Mitotic stage. It consists of time periods.
Cell formation occurs in several stages.
Phases
Mitosis is divided into several phases:
- telophase;
- anaphase;
- metaphase;
- prophase.
These phases proceed in a certain sequence and have their own characteristics.
In any complex multicellular mitosis, most oftenimplies the division of cells according to the undifferentiated type. With mitosis, the mother cell is divided into children, usually two. One of them becomes a trunk and continues division, and the second ceases to divide.
Interphase
Interphase is the cellular preparation for separation. Usually this stage lasts up to twenty hours. At this time, many different processes occur, during which the cells are prepared for mitosis.
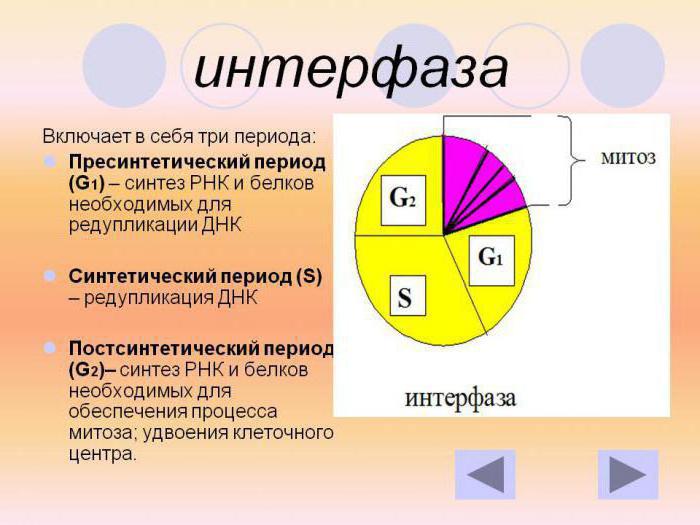
During this period there is a division of proteins,the number of organelles in the DNA structure increases. By the end of the division, genetic molecules are doubled, and the number of chromosomes does not change. Identical DNAs are fused and are two chromatids in one molecule. Formed chromatids are identical and are sister.
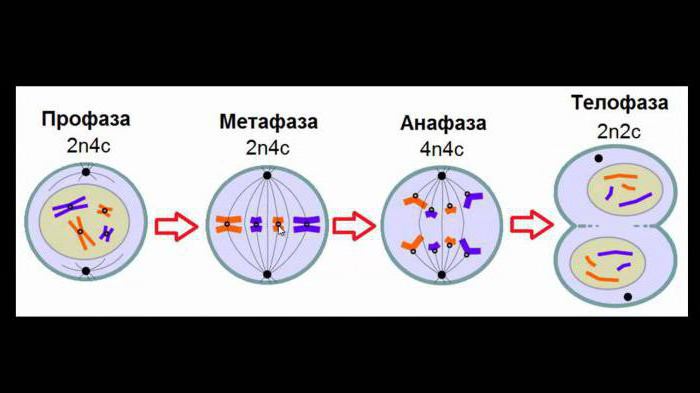
After the interphase is complete, mitosis itself begins. It consists of prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.
Prophase
The first phase of mitosis is prophase. It lasts about an hour. It is conditionally divided into several stages. At the initial stage in the prophase of mitosis, the nucleolus increases, as a result of which molecules are formed. By the end of the phase, each chromosome consists of two chromatids. The nucleoli and nuclear membranes dissolve, all elements are in the cell in disorder. Further in the prophase of mitosis, the formation of achromatin division occurs, part of the filaments pass through the whole cell, and some are connected to the central elements. In this process, the content of the genetic code remains unchanged.
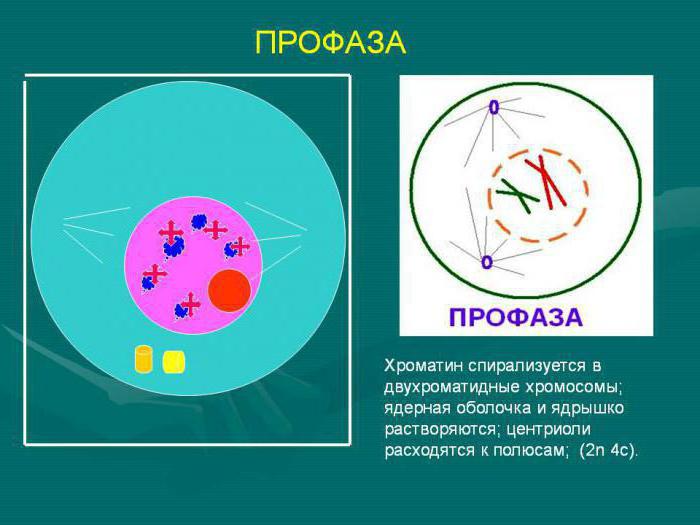
The number of chromosomes in the prophase of mitosis does not change. What happens yet? In the prophase of mitosis, the nuclear envelope decays, as a result of which the spiral chromosomes appear in the cytoplasm. Particles of the disintegrated nuclear shell form small membrane vesicles.
In the prophase of mitosis, the following occurs: the cell of the animal becomes round, and in plants it does not change shape.
Metaphase
After the prophase the metaphase comes. In this phase, the spiralization of chromosomes reaches its peak. The truncated chromosomes begin to move toward the center of the cell. During travel, they are located equally in both parts. A metaphase plate is formed here. When you look at the cell, you can clearly see the chromosomes. It is in the metaphase that they are easy to calculate.

After the formation of the metaphase plate, an analysis is made of the chromosome set inherent in this type of cell. This occurs by blocking the discrepancy of chromosomes with the help of alkaloids.
Each organism has its own set of chromosomes. For example, maize has 20, and in garden strawberry - 56. In the human body, chromosomes are less than berries, only 46.
Anaphase
All processes occurring in the prophase of mitosis,end, and anaphase begins. During this process, all chromosomal connections are broken and begin to move to opposite sides. In anaphase, the related chromosomes become independent. They fall into different cells.
The phase ends with a divergence to the poles of the chromatid cell. Also here is the distribution of hereditary information between the daughter and the mother cell.
The telophase
Chromosomes are located at the poles. Under the microscope, it becomes difficult to see them, since around them a shell of the nucleus is formed. The spindle of division is completely destroyed.
In plants, the membrane forms in the center of the cell, gradually spreading to the poles. She divides the mother cell into two parts. Once the membrane has fully grown, a cellulose wall appears.
Features of mitosis
Cell division may be inhibited byhigh temperatures, the effects of poisons, radiation. During the study of cell mitosis in different multicellular organisms, it is possible to use poisons that inhibit mitosis at the stage of metaphase. This allows you to study the chromosomes in detail, to perform carotomy.
Mitosis in the table
Consider the phases of cell division in the table below.
The phase of mitosis | Processes |
Metaphase | Accumulation of chromosomes |
Anaphase | Chromosomes diverge from the center of the maternal cell to the poles |
The telophase | Formation of nucleoli, end of division |
The process of mitosis stages can also be traced according to the table.
Phase Phase | Processes |
Presynthetic | Protein forms |
Synthetic | Doubling DNA |
Post-Synthetic | Synthesis of protein, preparation for division |
The first phase of cell division or prophase | The chromatization of the chromatids, the formation of the nucleoli |
Mitosis in animals and plants
Features of this process can be described in a comparative table.
Process | Plants | Animals |
Centrioles | No | there is |
Cellular plate | there is | No |
Bracing | No | there is |
The process of mitosis occurs | In meristems | In different parts of the body |
So, we considered the process of cell division in animal organisms and plants, as well as their features and differences.
</ p>