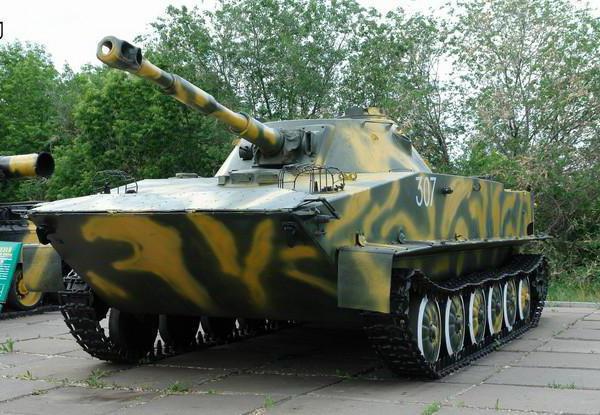
PT-76 floating tank: description, characteristics and interesting facts
Before the Second World War in the SovietThe Union had a lot of experience in creating floating armored vehicles. In the forty-first year, the Red Army had the largest fleet of such equipment, but during the fighting, the overwhelming majority of the specimens were destroyed by enemy troops. The remaining cars clearly did not meet the goals of the government and could strengthen the army a little. The PT-76 was a floating tank, the serial production of which was established in the post-war years. Several modifications have been made on its basis. Consider the characteristics and characteristics of amphibians.

History of creation
The floating tank PT-76 was planned to be equipped withgun caliber 76 mm. He had to be able to transport a solid stock of ammunition and be able to transfer to armor up to two dozen paratroopers. The design of the shipbuilding plant in Nizhny Novgorod (Krasnoye Sormovo) was engaged in the development of new technology.
The first pair of prototypes was made in1948 year. Unfortunately, the models did not pass the testing, after which the design was taken up by the All-Russian Research Institute of Transport Engineering in St. Petersburg (Leningrad). The Stalingrad transport plant was appointed the manufacturing enterprise. The overall project management was carried out by J. Ya. Kotin. At one time under his management, heavy self-propelled artillery installations were created. In the role of the leading designer was Shamshurin NF
The new project received an index of 740. By the summer of 1950, they produced prototypes. In severe tests, the new combat vehicle overcame its competitor (K-90 from Moscow manufacturers), having successfully passed all obstacles. In August 1951 the object was named "floating tank PT-76" and was adopted for service.
Structural features
The military machine under consideration possesses a classic layout, refers to an easy class. The armored case is equipped with three compartments:
- Department of Management, located in the bow.
- The combat compartment, located in the center of the hull, equipped with a conical configuration tower.
- Power section in the stern of the hull. There is a diesel engine and a pair of water jet propellers (first used on the basis of this technique).

In serial production the machine was launched already in 1951. Mass production continued until 1967. A total of about four thousand copies left the assembly line. In 1967, the technology was withdrawn from the armament.
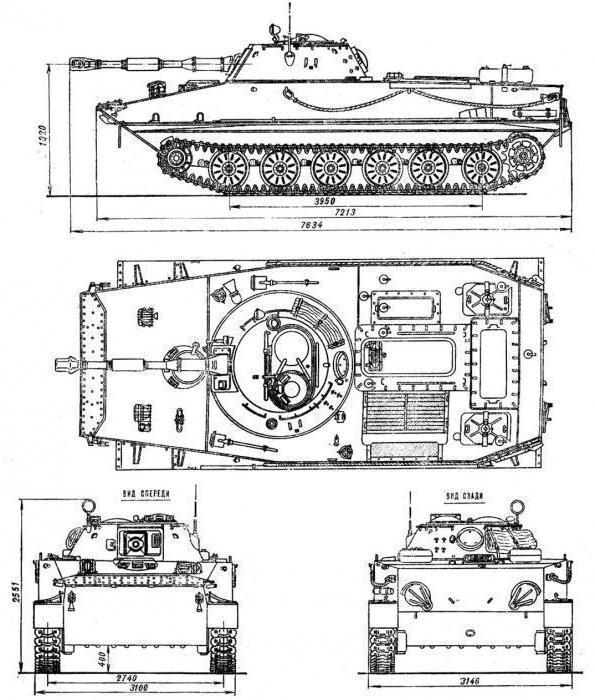
The PT-76 tank: characteristics
Below are the characteristics of the tactical and technical plan:
- The type of machine is a floating tank.
- Year of manufacture - 1951.
- The crew consists of three people.
- The layout is classical.
- Length / width / height - 6,91 / 3,18 / 2,19 m.
- The thickness of armor - from 5 to 13 mm, depending on the location (nose, side, bottom, tower).
- Base - 4.08 m.
- The track is 2.74 mm.
- Road clearance - 37 cm.
- Type of armor - rolled homogeneous of steel with increased strength.
- Armament - rifled gun caliber 76 mm, machine gun SGMT caliber 7.62 mm.
- The range of the shot is up to 12 km.
- Type of sight - Telescopic brand TShK-66.
- Power plant - diesel engine V-6 with a capacity of 240 horsepower.
- The speed indicator (maximum) is 44 km / h overland, 10.2 km / h - afloat.
- Weight - 14 tons.
- The overcoming moat is 2.8 m.
- The range for cross-country / afloat is 210/70 km.
- Suspension - individual torsion type.
- Specific power - 17.1 liters. c / t.
Observation and communication devices
The lightweight floating tank PT-76 is equipped with threeperiscopic devices, which are placed in the rotating turret of the commander. The attachments are tightly mounted and provide a qualitative overview of a rather narrow sector.

Instruments have a fivefold increase and a fieldview of 7,5 degrees on the horizon. On the sides there are periscopes of TNP with a single magnification. Charging for the survey of the terrain can use only one rotary device of a single increase in MK-4. It is in front of the hatch in the tower roof.
In non-combat conditions, the driver-mechanic leadsObservation of the terrain through an open hatch. In combat conditions, three devices of the TNP type serve as a review. To control the car in conditions of poor visibility or at night, a binocular night vision device TVN-2B is provided. It includes an infrared filter, electronic stuffing and optics. The range of vision is about 60 meters, with a viewing angle of not more than 30 degrees.
Tank PT-76: description of the engine and undercarriage
By and large, the power unit of theThe amphibian is a modernized motor of the T-34 tank. The gearbox is also borrowed from this model. A decent speed and good maneuverability on the water provide water jet propulsion. Thanks to these elements, the floating tank PT-76 could easily overcome water bodies overgrown with shrubs.
At the same time, a low specific pressuretrucks to the ground, which guaranteed the car easy crossing of heavily waterlogged areas. The fighting amphibian became more compact and easier to maintain, and also received hydraulic shock absorbers interacting with an individual torsion suspension. These nodes provided the technician with improved ride and increased cruising speed. The floating tank PT-76 C 60 was equipped with a system of protection against WMD and an automatic fire-fighting device. The technique showed itself well in forced marches with a range of up to 500 kilometers.

Modifications
Several modifications have been made on the basis of the machine under consideration. Among them:
- The model with a 76 mm D-56TM guntwo-chamber muzzle brake. In addition, she had an ejector, an internal walkie-talkie, a night vision device, an anti-smoke thermal device. The height of the case is increased by 13 millimeters. The year of improvement is 1957.
- The upgraded PT-76B was released in 1959. It is equipped with a two-plane gun D-56TS, stabilizing device STP-2P, ventilation unit with filters. On later versions, a gyro compass was installed.
- In 1967, the PKT course machine gun, the P-123 intercom, was installed on the tank under consideration. The machine was in service with reconnaissance corps and in the Marine Corps.
- On the basis of PT-76, an armored personnel carrier BTR-50, launchers for Luna missile complexes, and a UR-67 division for mine clearance were created.

Interesting Facts
The first serious combat encounter PT-76was held in March 69 in Vietnam. A team of twelve vehicles and armored personnel carriers attacked the American base of Ben-Hat with the aim of destroying the cannon battery. The head PT-76 was blown up on a mine, but the crew did not fail and continued to fire. The rest of the cars entered into confrontation with the Patton platoon and a pair of anti-aircraft self-propelled vehicles. Losses suffered both sides, but the attack did not continue after the loss of two tanks and one APC.
In the spring of the year 65, India appealed to the USSR forhelp to get protection from a possible invasion of Pakistan. The first batch of amphibians India received in the summer of the 65th. In total, the country had two regiments of such machines with a total number of about 90 copies.
In September 1965 Brigade PT-76 in the seventh Indian machine-gun regiment attacked the Pakistani-captured village. As a result, the enemy managed to knock out, losing one tank from his side. During the war, India lost near the PT-76 company, some of which were captured by the army of Pakistan.
Participation in other military conflicts
Among the most famous confrontations involving the machine in question, the following armed conflicts can be noted:
- The war between India and Pakistan in 1971. In fourteen days of fighting, 13 PT-76 tanks were destroyed and damaged, and the Pakistanis lost all their heavy vehicles. This was one of the weighty contributions to the victory.
- The 1967 war (six-day) between Egypt andIsrael. The Egyptians had 29 machines in the arsenal. However, they were used for other purposes. As a result, two units were destroyed, 7 - abandoned. The captured models were redesigned and installed on them by American weapons.
- The war of the day of judgment in 1973. In it, PT-76 participated both from Egypt and from Israel.
- In addition, the cars took part in the Yugoslav wars and the confrontation in Chechnya.
In conclusion
Now a lightweight floating tank PT-76 and BTR-50 -magnificent and unnecessary "floats". In the USSR, they were removed from service in 1967. Nevertheless, the decommissioned cars gained popularity among the countries of the Middle East and were actively used. For its time, this technique has proved very successful, both on land and on water.

Lightweight floating tanks were actively exported tothe Warsaw Treaty states, as well as the majority of pro-Soviet African and southeastern countries. The captured Egyptian cars were modernized by Israeli engineers, and China produced its own analogue under the "type-63" index.
</ p>




