CHP: decoding. Cogeneration plants (CHP)
Provision of population with heat and electricityis one of the main tasks of the state. In addition, without the production of electricity, it is impossible to imagine a developed manufacturing and processing industry, without which the country's economy can not exist in principle.

Features
That's what a CHP plant is. Deciphering the concept you already know. But what features does this kind of power plant have? After all, it is no coincidence that they are singled out as a separate category !?
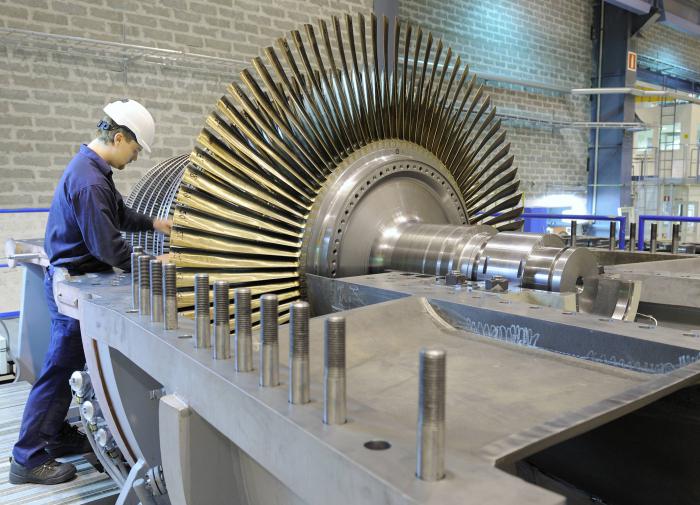
The fact is that they produce not onlyelectricity, but also heat, which is supplied to consumers in the form of hot water and steam. It should be noted that electricity is a by-product, since steam, which is supplied to heating systems, first rotates the turbines of the generators. Combination of two enterprises (boiler and power plants) is good because it is possible to significantly reduce fuel consumption.
However, this also leads to quite aa small "distribution area" of the CHPP. The decoding is simple: since not only electricity is supplied from the station, which can be transported to thousands of kilometers with minimal losses, but also a heated coolant, they can not be located at a significant distance from the settlement. Not surprisingly, almost all CHP plants are built in close proximity to the cities where they heat and light the inhabitants.
Ecological significance

The newest cleaning equipment allowsit is effective to purge the release, and the energy efficiency of such a solution is extremely high. Thus, the energy released from burning a ton of oil is identical to the volume that is released when recycling two tons of plastic. And this "good" is enough for tens of years to come!
Most often, the construction of a CHP plantThe use of fossil fuels, as we mentioned above. However, in recent years, it is planned to create nuclear power plants, which will be installed in the hard-to-reach regions of the Far North. Since fuel delivery there is extremely difficult, nuclear power is the only reliable and constant source of energy.
What are they like?
There are CHP (photo of which is in the article)Industrial and "household", heating. As it is easy to guess from the name, industrial power plants provide electricity and heat to large industrial enterprises.
Often are built at the stage of erection of the plant,making together with it a single infrastructure. Accordingly, "household" varieties are erected near the sleeping microdistricts of the city. In industrial CHP, heat is transferred in the form of hot steam (no more than 4-5 km), in the case of heating - using hot water (20-30 km).
Information about equipment of stations
The main equipment of these enterprises areturbine units that transfer mechanical energy into electricity, and boilers responsible for generating steam that rotates the flywheels of the generators. The turbine unit includes both a turbine and a synchronous generator. Tubes with a back pressure of 0.7-1.5 MN / m2 are put on those CHP plants that supply heat and power to industrial facilities. Models with a pressure of 0.05-0.25 MN / m2 serve to provide household consumers.
Efficiency issues

Condensing type plants
In this case, to supply consumers with heatonly so-called "steam of selection" is used, and all other heat is often simply lost, dissipating in the environment. To reduce energy losses, such CHP should operate with minimal heat output to the condensing unit.
However, since the times of the USSR, suchstations in which the hybrid mode is constructively provided: they can operate as conventional condensing thermal power plants, but their turbine generator is quite capable of functioning in a back pressure mode.
Universal varieties
It is not surprising that the installation withcondensation of steam have received the maximum distribution due to its universality. So, only they enable practically independently to regulate electric and thermal load. Even if the heat load is not expected at all (in the case of a particularly hot summer), the population will be supplied with electricity according to the previous schedule (Western CHP in St. Petersburg).
"Thermal" types of CHPP

Heat release in most cases istwo schemes. If an open version is used, the hot steam from the turbines goes directly to the consumers. In the event that a closed circuit was selected, the coolant is supplied after passing the heat exchangers. The choice of the scheme is determined on the basis of many factors. First of all, the distance from the object provided by heat and electricity, the amount of population and season is taken into account. So, the South-Western TPP in St. Petersburg operates in a closed system, as it provides greater efficiency.
Characteristics of the fuel used
A solid, liquid andgaseous fuel. Since CHP plants are often built in close proximity to large settlements and cities, it is often necessary to use its valuable types, gas and fuel oil. The use of coal and garbage as such in our country is rather limited, since not all stations have modern efficient air-cleaning equipment.
To clean the exhaust of the plants,special particle traps. In order to dissipate solid particles in sufficiently high layers of the atmosphere, pipes are built at a height of 200-250 meters. As a rule, all cogeneration plants (CHP) stand at a sufficiently large distance from water supply sources (rivers and reservoirs). Therefore, artificial systems are used, which include cooling towers. Direct supply of water is extremely rare, in very specific conditions.
Features of gas stations

There, these stations play two roles at once: provide the supply of the population with electricity and industrial water, as they simultaneously serve as desalters for sea water. And now we will consider the main thermal power stations of our country and the near abroad.
South-West, St. Petersburg
In our country, WesternCHP, which is located in St. Petersburg. It is registered as OJSC "Yugo-Zapadnaya CHPP". The construction of this modern facility pursued several functions at once:
- Compensation of a strong deficit of thermal energy, which hindered the intensification of the housing construction program.
- Increasing the reliability and energy efficiency of the city system as a whole, since St. Petersburg was the problem with this aspect. The CHP allowed us to partially solve this problem.
But this station is also known for the fact that one of thethe first in Russia began to meet the strictest environmental requirements. For the new enterprise, the city government allocated an area of more than 20 hectares. The fact is that the reserve area was reserved for the construction, remaining from the Kirov district. In those parts there was an old collector of ash from CHPP-14, and therefore the district was not suitable for housing construction, but extremely well located.
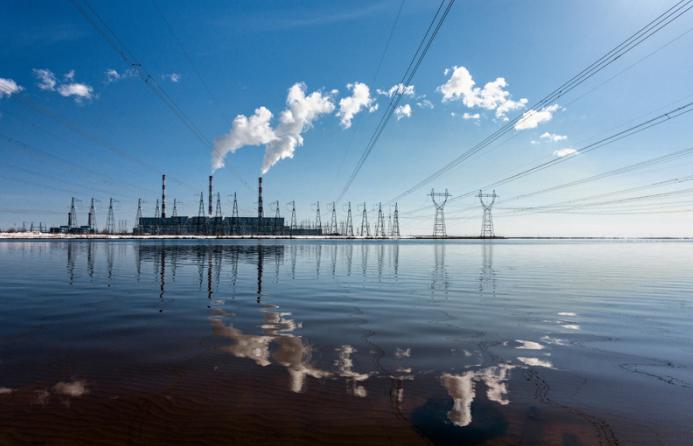

Murmansk
The city of Murmansk is known as the base of our fleet atThe Baltic Sea. But it is also characterized by extreme severity of climatic conditions, which imposes certain demands on its energy system. It is not surprising that the Murmansk thermal power station is in many respects a completely unique technical object, even in the whole country.
It was put into operation in 1934,and since then continues to regularly supply residents of the city with heat and electricity. However, in the first five years Murmanskaya CHPP was a conventional power plant. The first 1150 meters of the heating main were laid only in 1939. The case in the neglected Nizhne-Tuloma HPP, which almost completely covered the city's electricity needs, and therefore it became possible to release part of the heat output for heating the city's houses.
The station is characterized by the fact that the whole year it works inbalanced mode, since its thermal and "energy" yields are approximately equal. However, in the conditions of the polar night, the CHP plant, at some peak moments, starts using most of the fuel just for electricity generation.
Novopolotsk station, Belarus
Design and construction of this objectbegan in August 1957. The new Novopolotsk CHPP was supposed to solve the problem of not only the heat supply of the city, but also the provision of electricity to the oil refinery that was being built in the same area. In March 1958 the project was finally signed, approved and approved.
The first stage was put into operation in 1966. The second was launched in 1977. At the same time Novopolotsk CHP was modernized for the first time, its peak capacity was increased to 505 MW, and a little later laid the third stage of construction, completed in 1982. In 1994 the station was transferred to liquefied natural gas.
To date, the modernization of the enterprisealready invested about 50 million US dollars. Thanks to such impressive cash injections, the company was not only fully transferred to gas, but also received a huge amount of completely new equipment, which will allow the station to serve for tens of years.
conclusions

- Landfills are unloaded and cleared.
- The city receives cheap electricity.
- The problem with heating is being solved.
In addition, coastal areas are quite realisticthe construction of CHP plants, which will simultaneously act as desalters of seawater. Such a liquid is quite suitable for irrigation, for livestock complexes and industrial enterprises. In a word, the real technology of the future!
</ p>