Rodnichok in infants as an indicator of health
The children's fontanel is a characteristica feature of the structure of the skull of a newborn baby. It is a soft area on the parietal part of the head between parts of the skull. This area has no bone tissue, but is closed by a strong membrane. A rodlet in infants enables the bones of the skull to contract during childbirth during the passage of the baby through the birth canal.
What are the fontanelles of newborns?
Newborn children have six fontanelles. The largest is the front, the second largest is the rear. There are two mastoid and two wedge-shaped. Open after childbirth, there are usually two main fontanelles: frontal (large) and occipital (small).
Sizes of children's fontanelles
The large fontanel resembles the shape of a rhombus. Normal is considered if its size is within 1-3 centimeters. Most often, such fontanel in children is 1.7-2.5 centimeters. And at the age of three months it decreases to 1-1.5 centimeters.
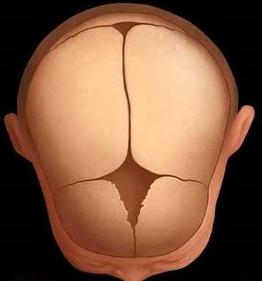
Timing of ferns closing
Four lateral fontanel in full-term childrenclose to the birth, in preterm - for the first few days after birth. The occipital fontanel in infants is completely closed in 2-3 months. But there are no exact dates for closing the largest fontanel. This is a very individual process. He can grow to 12 months, and maybe 1.5 and 2 years. In recent years, due to the acceleration of children, the frontal fontanelle disappears by 10 months.
What is the reason for the early closure of the frontal fontanel?
The earliest is the closure of the fontanel earlierthe third month of the baby's life. Usually this is due to the enthusiasm of the future mother by taking multivitamins and calcium-rich foods, which results in small and fairly dense fontanel in the child. Therefore, you should observe the norm in taking vitamins by the time of pregnancy.
Than it is dangerous?
Early closure of the fontanel has a significant effect on the full development of the brain, interfering with its normal growth. The danger is that the early overgrown

What is the reason for the closure of the fontanel?
Later, the closure of the frontal fontanelle is associated with a low calcium content in the body. The lack of calcium limits the intake of vitamin D3. And this leads to a change in bone tissue.
Than it is dangerous?
By itself, the closure of the fontanel does not speak of danger. It is important to study and accompanying symptoms, as this can be a dangerous signal.

What else can "tell" fontanel?
There are several "signals" that can not be ignored:
fontanel in infants sinks - the body lacks fluid;
for a long time it is "convex" - increased intracranial pressure;
increased size - a violation of ossification or prematurity.




