Introductory seventh chord: what is it, what are, what kind of treatment and permission do they have?
From the article you will find out what the seventh chord is, itstypes of structure. In more details, introductory seventh chords will be considered: small and small. You will learn how to properly build them, what kind of treatment they have and where to solve them.
What is a seventh chord?
Before considering what the opening seventh and dominant chords are, what they are, what appeals are and where they are resolved, we should turn to the concept of the seventh chord as such.
This is a chord (or such a consonance), which contains four sounds. All of them are located on a large or small third.
Its name arose not by chance. The first and last sounds of the seventh chord are the seventh - the musical interval.
The four-sound of this chord makes it specialunstable and requiring compulsory authorization. In classical music, all kinds of seventh chords are used for its dynamization. In modern music, they are very widely used.

The sounds of this chord are called the same as the intervals that are formed from the main tone. These are: prima (main tone), thirds (tertiary tone), quinta (quintal tone), and septima.
Types of seventh chords in the structure
- Big major. The basis is a major triad. The first and last sounds cover a large seventh.
- Small major. The basis is a triad of majeure. The first and last sounds span the interval of a small septum.
- Small minor. A sobering minor is at its core. The first and last sounds cover a small seventh.
- The big minor. The basis is a minor triad. The first and last sounds cover the interval of a large septum.
- Small reduced. It is also called semi-reduced. The basis of this seventh chord is a reduced triad. The first and last sounds span the interval of the reduced sept. Sounds the same as a minor minor. If you build it, you will see that it is identical with it.
- Reduced. The basis is a reduced triad. The first and last sounds span the interval of the reduced sept.
- Increased. It is also called a large magnified. The basis is an increased triad. The first and last sounds cover a large seventh.
What is the introductory seventh chord?
This seventh chord is built on all fret steps. You probably know the dominant seventh chord. It is built on the fifth step. Also, everyone knows the second-degree seventh chord, which has no special name.

But the four-sound chord built in harmonyon the seventh step, has its name - the opening seventh chord. He received it thanks to the degree on which it is built. It, in fact, is introductory, because it is very unstable and very tends to tonic.
Varieties of the introductory seventh chord
There are two types: small and small.
Small introductory seventh chord in structure and soundis equal to a small reduced (half-reduced). It is built only in natural major on the seventh step. It is based on a reduced triad. The first and last sounds of this seventh chord span the interval of the small seventh. It is formed from two small thirds and one large or smaller triad and a large third.
Its construction in the F-major is natural: e-g-b-d. Mi (e) and pe (d) are extreme sounds that form the interval of a small septum.
Reduced introductory seventh in naturalfrets not built. Its construction is possible in a major and minor harmonic from the seventh step. At its basis, as in the small introductory, is a reduced triad. The first and last sounds cover the interval of the Septima reduced.
Its construction in the F-major is harmonic: e-g-b-des. Where des (re flat) is the sixth lowered level of the harmonic major. A mi-re flat - this is the first and last sounds that make up the interval of the reduced Septima.
In harmonic harmonic: fis-a-c-es. Where fis is the seventh raised stage of the harmonic minor. And fis-es are the extreme sounds of the mind.
Appeals and Permissions

The introductory seventh chord, like any other, contains three references. This is a quintecstack chord (6/5), a tertzquart chord (4/3) and a second chord (2),
The seventh-stage quintecstack chord is designated VII6 / 5. It is built on the second step. VII6 / 5 small in C major (n): d-f-a-h. VII6 / 5 reduced in C major (d): d-f-as-h. In the A minor (d): gis-h-d-f.
Tertzkartakkord seventh stage is designated VII4 / 3. It is built on the fourth step. VII4 / 3 small in F major (n): b-d-e-g. VII4 / 3 reduced in F major (d): b-des-e-g. In the D minor (d): g-b-cis-e.
A seventh-stage second-order second is denoted by VII2. It is built on the sixth step. VII2 small in the major-major (n): e-fis-a-c. VII2 reduced in the major-major (d): es-fis-a-c.
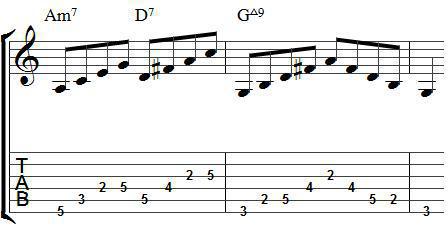
There are two options for resolving introductory seventh chords. The first - immediately into the tonic. The second - through the dominant seventh in the tonic.
Thus, the introductory seventh chord consists offour sounds that are located over a large or small third. There are two types: small and small. They have the same treatment as all the other seventh chords, only with the indication of the seventh degree. Permits are of two kinds. Direct - immediately into the tonic. And through the chords of the dominant group.
</ p>




