Irritability is ... Irritability and excitability
Irritability is the ability of the body orindividual tissues respond to the environment. It is also the ability of the muscle to contract in response to stretching. Excitability refers to a property of a cell that allows it to respond to stimulation or stimulation, for example, the ability of nerve or muscle cells to respond to an electrical stimulus.

The most important biological property
Irritability is in biology the property of tissues,who can perceive an internal or external intervention and respond to it by going into an excited state. Such tissues are called excitable and have a certain number of characteristic qualities. They include the following:
1. Irritability. This is when cells, tissues and organs are capable of responding to the intervention of certain stimuli, both external and internal.
2. Excitability. This is a quality of animal or plant cells, in which it becomes possible to change the state of rest to the state of physiological activity of the organism.
3. Conductivity. This is the ability to spread excitatory reactions. It depends on the structure of the tissue and its functional characteristics.
4. Memory is responsible for fixing the occurring changes at the level of molecules with the introduction of changes in the genetic code. This quality makes it possible to foresee the behavior of the organism in response to repeated interventions.

Irritability: definition and description
What is irritability? Is this property of the body the norm or is it rather a state of painful excitability and excessive sensitivity of the organ or part of the body? Natural susceptibility is characteristic of all living organisms, tissues and cells, which, under the influence of certain stimuli, react in a certain way. In physiology, irritability is the property of the nervous, muscle or other tissues to react to stimuli. The ability to respond to changes in the physical or biological environment is a property of all life on Earth. Examples are the following: the movement of plants to light, the constriction and dilatation of the pupil due to a change in the intensity of light and so on.

The etymology of the concept
The term comes from Latin irritabilitas. Irritability is the reaction of excitation to certain external factors. This term is used to describe physiological reactions to stimuli, as well as pathological manifestations associated with excessive sensitivity. This concept should not be confused with irritability.

Irritability and adaptation
All living organisms possess the following property:irritability. It is the ability of the body to perceive and respond to certain stimuli that can have both positive and negative effects. The plant usually tends to the side where there is more sunlight. Feeling warm, a person can remove his hand from a hot stove.
Closely related to the concept of "irritability"is an adaptation that is responsible for changes in the body in response to external influences. For example, the human skin darkens when exposed to intense sunlight. The term "adaptation" is often used to describe certain changes in populations that, as a rule, can not be transferred to the offspring and therefore are not evolutionarily significant. In addition, these changes are usually reversible. For example, sunburn will gradually disappear if the individual ceases to stay in the sun. Environmental conditions can also cause long-term changes in the genetic composition of the population, which will be irreversible in individual organisms.
Basic concepts
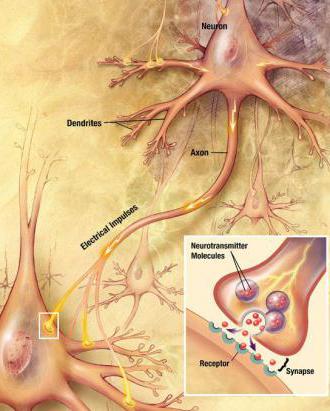
Irritability is called the ability of the livingorganisms to react in a certain way to external influences by changing their form and some functions. In the role of irritants are those environmental factors that can cause a response. In the course of evolutionary development, tissues that have an increased level of sensitivity due to the presence of special receptors in the cells have been formed. Such susceptible tissues include nervous, muscular and glandular tissue.

Interrelation of irritability and excitability
Irritability and excitability are inextricably linkedbetween themselves. Excitability refers to the property of highly organized tissues, as a reaction to external influences by changing physiological qualities. In the first place of excitability will be the nervous system, followed by muscles and glands.
Types of irritants
There are external and internal ways of intervention. External are:
- Physical (mechanical, thermal, ray and sound). Examples can be sound, light, electricity.
- Chemical (acids, alkalis, poisons, drugs).
- Biological (bacteria, viruses and the like). An irritant can also be considered food and an individual of the opposite sex.
- Social (for people it can be ordinary words).
As for the domestic, it is aboutsubstances that are produced by the body itself. It can be hormones and other biologically active components. Three groups are distinguished according to the strength of the impact: subthreshold - those that may not elicit response, threshold - moderate intensity interventions - and superthreshold, causing the strongest reaction.
</ p>



