Structure of cells of fungi. Types of fungi: mold and yeast
The nature of mushrooms has always caused a lot of questions. In this article we will try to understand this and learn about the peculiarities of the structure of the fungal cells.
What are fungi: plants or animals?
In the first half of the 20th century, mushrooms wereplants. Detailed studies have shown that they do not possess the main feature of plants, namely the ability to photosynthesize, but they have much in common with animals. But this statement was also refuted. In 1969, scientists came to the conclusion that the structure of the cells of fungi has its own unique characteristics, and therefore they should be attributed to a separate realm of living nature.

By tradition, the science of mycology is a sectionbotany. Like most organisms, fungi belong to the supercarship of eukaryotes, or nuclear ones. Their peculiarity consists in the synthesis of qualities that are inherent in other living beings. Like plants, they do not have arms, legs, eyes, independent movement for them is also difficult. Together with this fungi are deprived of the ability to produce organic substances. Like animals, they consume them in ready-made form.
This is one of the most diverse biologicalgroups. Counting the total number of species that are included in this kingdom is difficult even for specialists. The figures range from 300 thousand to several million. Mushrooms are a part of all terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.
Structure of fungal cells
The average size of the fungal cell in diameter isfrom 10 to 100 μm. Outside, it is enveloped by a strong shell, or a cell wall. It consists of polysaccharides, lipids, phosphates, simple sugars, proteins, chitin and other substances. Inside the wall is covered with a plasma membrane, which is responsible for the metabolism and maintenance of pressure.
The membrane is filled with a liquid - cytoplasm, inwhich are all organelles. In the form of small particles in the cytoplasm is glycogen with a supply of nutrients. The basis of the cell is the nucleus, it contains genetic information. There may be several, depending on the type of fungus. Sometimes the nucleus is the nucleolus.
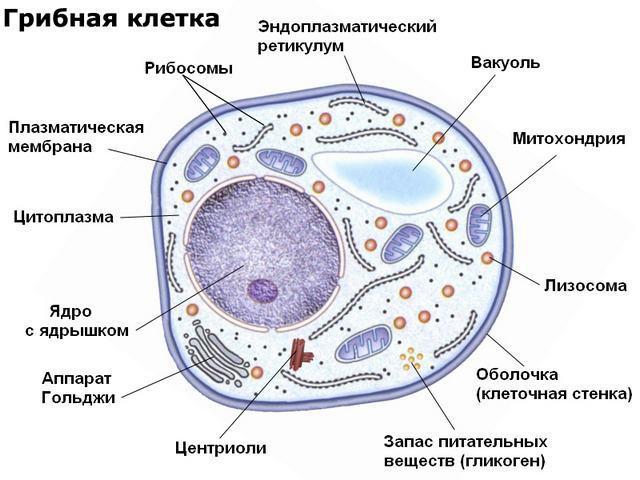
The structure of fungal cells is also characterizedthe presence of vacuoles, centrioles, mitochondria, and lobas. They contain the Golgi apparatus along with its various derivatives, for example, phagosomes and lysosomes. The main task of all its components is the chemical rearrangement of secretion products. The endoplasmic reticulum is represented in the fungal cell by a branched network of tubules and tubules that perform many functions. Among them - the accumulation of carbohydrates, neutralization of poisons, the synthesis of hormones.
The structure of the cell of the fungus is presented to your attention above.
Distinctive features in the structure
Together with plants and animals, the fungi belong toeukaryotes due to the presence of nuclei in their cells. In this regard, the cellular structure of these organisms has similarities. The animals and plants have the most different composition, while the structure of the fungal cells is something average.
They, like plants, have a solid cellularshell. Only it consists not of cellulose, but of chitin, which is present in some animals (crayfish, insects, etc.). Fungi do not have chloroplasts and can not carry out photosynthesis. Like plants, mushroom cells contain vacuoles, and instead of starch, glycogen.
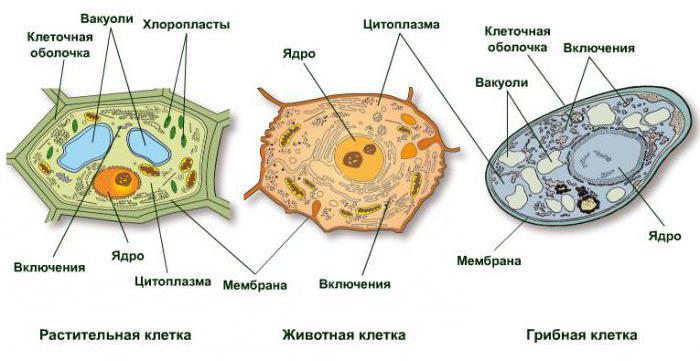
The main common feature of mushrooms and some animalsis the presence of chitin, as well as the accumulation of glycogen polysaccharide as a nutrient. Representatives of both kingdoms have heterotrophic nutrition. Animal cells, in contrast to fungi, do not have vacuoles and dense cell walls, except the protective membrane.
Mold fungi
Among the huge variety of mushrooms are andmold, scientifically - oomycetes. No different from other types of cells of mold fungi. The structure of these organisms has external differences. They do not have a pronounced fetal body (reproductive organ), like that of the mushrooms. All that can be seen with the naked eye is a highly branched mycelium, which usually hides beneath the ground behind the hat mushroom. The fetal body is weakly expressed in mold.
The main distinguishing feature ismicroscopic size. These organisms are widely distributed throughout the world. The mold was found even in the ice of Antarctica. These mushrooms reproduce by spores and especially love moisture. They are characterized by high survival and adaptability to various environmental factors. Mold does not kill even radiation. There are species that can cause great harm to humans and animals (aspergillosis, etc.), and some are used as antibiotics (penicillin, cyclosporine).
Yeast
One type of fungi is yeast. Unlike the hat and fungi, they usually do not form a mycelium. Reproduction of this species occurs not by arguments, as in their "relatives", but by a vegetative method by means of division or budding. Some species still form a mycelium, which can decay into single cells.

Yeasts have the ability to decompose sugar intocarbon dioxide and alcohol. This process is called fermentation. When it is carried out, the necessary energy is released for the life of the fungus. Fermentation helps to raise the dough, making it porous, so it is often used in cooking.
Yeasts are demanding for environmental conditions. For them, the presence of sugar in the substrate is important. They are distributed on the surface of fruits and leaves, in natural water bodies and soils. Individual species inhabit the intestines of insects that feed on wood.
</ p>




