Scheme of a small circle of blood circulation in mammals
Circulatory and respiratory systems are connected betweenstructurally and functionally. Together they provide the vital functions of the body, allow the supply of tissues and organs with oxygen and nutrients. And since the first animals, partially conquered the land, there is a unity of these systems. It provides a higher level of structural organization and optimization of physiology to living conditions on land.

Respiratory and cardiovascular systemmammals, amphibians, birds and reptiles consists of lungs, heart and vessels. In this case, the scheme of the small circle of blood circulation is entirely represented by the lungs, that is, the pulmonary capillaries, to which blood enters the arteries, and is diverted through the veins. It is noteworthy that there are no structural barriers between the circulatory circles, because of which the respiratory tract and the cardiovascular system are considered a single functional block.
Sequential scheme of the small circle of blood circulation
A small circle is a closed chain ofvessels through which blood from the heart goes to the lungs and returns back. Moreover, despite the differences in the physiology of hemocirculation, the scheme of a small circle of blood circulation of mammals does not differ from that of amphibians, reptiles and even birds. With the latter, mammals have more in common than with the rest. In particular, we are talking about the 4-chamber heart.

Since the boundaries between the vessels of the body are notexists, then the right ventricle of the heart of the mammal is considered the conditional beginning of the small circle of circulation. From it, through the pulmonary trunk, blood deprived of oxygen is sent to the pulmonary capillaries. The processes of gas diffusion occurring in the alveolar epithelial cells are completed by the release of carbon dioxide into the lumen of the alveoli and the capture of oxygen. The latter combines with hemoglobin and is sent to the left heart by the pulmonary veins. As the scheme of the small circle of blood circulation shows, it ends in the left atrium, and the systemic blood flow starts from the left ventricle.

Small circle of blood circulation of birds
According to the physiology of respiratory and cardiovascularbird systems are most similar to mammals, since they also have a 4-chambered heart. Amphibians and reptiles have a 3-chambered heart. As a result, the scheme of a small circle of blood circulation of birds is the same as in mammals. Here, from the right ventricle, venous blood flows to the pulmonary capillaries. Oxygenation enriches the blood with oxygen, which is transported to the left atrium by erythrocytes with arterial blood, and from there to the ventricle and systemic bloodstream.
Pulmonary circulation of birds and mammals
Probably, it is necessary to understand what kind of blood flowsin the veins of the small circle of blood circulation in birds, mammals, reptiles and amphibians. So, in mammals, through the pulmonary artery, the venous blood flows to the capillaries, depleted in oxygen and containing carbon dioxide in large quantities. After oxygenation, arterial blood flows through the veins towards the heart. It is noteworthy that in the great circle of blood circulation arterial blood from the heart always flows only along the arteries, and the venous returns to the heart through the veins.
Pulmonary circulation of reptiles and amphibians
The scheme of the small circle of the frog's circulation is notdiffers from that in mammals. However, they are different in physiology: due to the presence of a 3-chambered heart, venous and arterial blood mix. Therefore, along the arteries of the body, including the pulmonary, a mixed biological fluid flows. And venous through the veins of the body returns to the heart, and then again mixed in a three-chambered heart. Therefore, the partial pressure of oxygen in the arteries of the small and large circle of blood circulation is practically the same. Therefore amphibians are cold-blooded.

Reptiles also have a three-chambered heart, butupper and lower sections of the common ventricle, there is a rudiment of the septum. At crocodiles and at all the septum between the right and left ventricle is practically formed. It has only a few holes. As a result, crocodiles are more hardy and larger compared to other reptiles. At the same time, it is not known what kind of heart the dinosaurs possessed, also belonging to the class of reptiles. Probably, they also had a practically full septum in the ventricles. Although evidence is unlikely to be obtained.
The analysis of the scheme of a small circle of a circulation of the person
In humans, gas exchange takes place in the lungs. Here the blood gives off carbon dioxide and is saturated with oxygen. This is the main significance of pulmonary blood circulation. Any academic scheme of the small circle of blood circulation, created on the basis of studies of the physiology of the respiratory system, begins with the right ventricle. Directly from the pulmonary valve leaves the pulmonary trunk. Due to its division into two parts, the branch of the pulmonary artery branches to the right and left lungs.
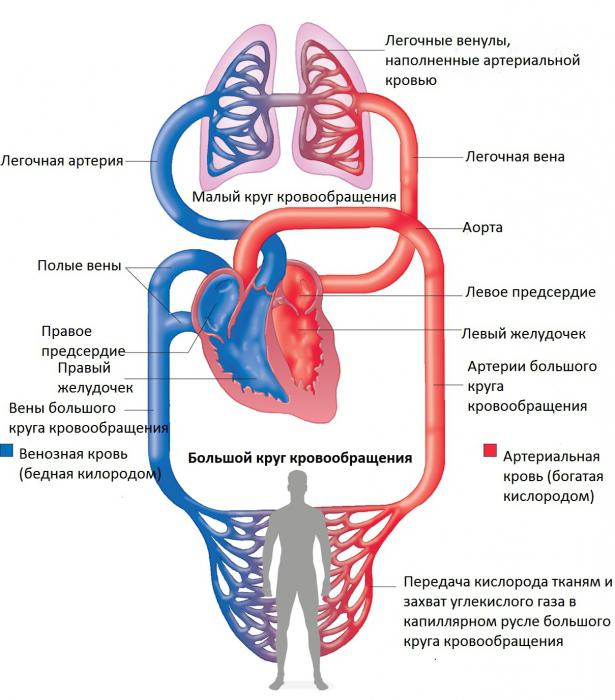
The pulmonary artery itself is divided many times andcrushed to the capillaries, densely piercing the tissue of the organ. Gas exchange takes place directly in them through the air-blood barrier, consisting of alveolar epithelial cells. After oxygenation of the blood, it is collected into venules and veins. Two leaves each lung, and the left atrium is already 4 pulmonary veins. They carry arterial blood. This completes the pulmonary circulation, and the systemic circulation begins.
Biological significance of the small circle of blood circulation
A small circle in phylogenesis appears in organisms,which begin to settle the land. In animals that live in water and receive dissolved oxygen, it is absent. Evolution has created another respiratory organ: first simple trachea lungs, and then - complex alveolar ones. And just with the appearance of the lungs, a small circle of blood circulation develops.
From this moment the evolution of the development of organisms,living on land, is aimed at optimizing the capture of oxygen and its transportation to consumer tissues. The lack of mixing of blood in the cavity of the ventricles is also an important evolutionary mechanism. Thanks to it, mammals and birds are warm-blooded. Also, more importantly, the 4-chambered heart provided brain development, because it consumes a quarter of all oxygenated blood.
</ p>



