Facial nerve: anatomy, pattern, structure, functions and features
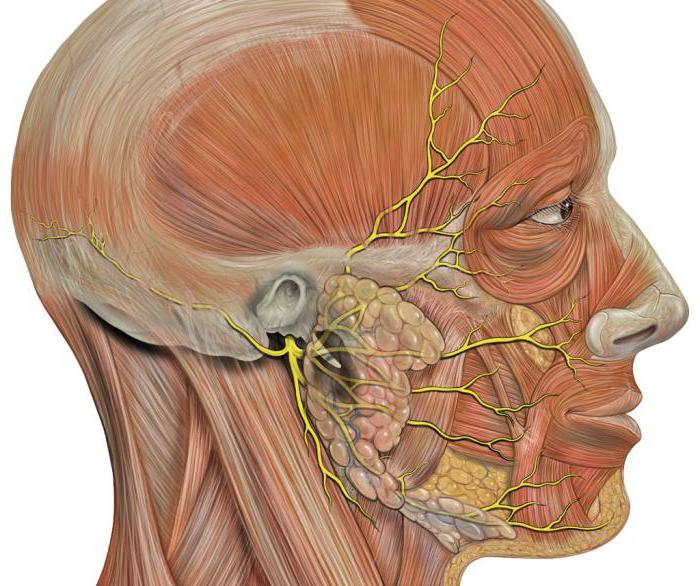
The topographic anatomy of the facial nerve is rather confusing, which is explained by the fact that it passes through the facial canal of the temporal bone, taking and giving out the processes.
Where does it originate?
It departs immediately from three cores: motor, secretory and sensitive fibers. Then, through the auditory opening, the facial nerve passes into the thickness of the temporal bone into the internal auditory canal. Here an intermediate nerve is added to it, and a knee is formed on the bend of the canal, which, taking the shape of the knot, gives the intermediate nerve a property of sensitivity. Anatomy of the facial nerve and the scheme will be discussed in this article.

Separation into sprouts
To enter the parotid gland, facialthe nerve is divided into separate outgrowths: the lingual branch, the posterior auric nerve, the two-abdominal and the shilo-lingual branch. Intermediate gives such branches as stenotic and stony nerves, connective tissue with a drum weave and with a vagus nerve, an end branch (a drum string). The anatomy of the facial nerve is unique.
Branches
One more time the facial nerve dissolves in the thicknessparotid gland, giving two main branches - a small lower and a powerful upper, which then also branch, and radially: upward, forward and downward to the muscles of the face. As a result, the parotid plexus is formed.
The facial nerve (the anatomy diagram will be presented in the photo) consists of the following parts:
- the nerve trunk (if more accurately, its processes);
- space cortex of the hemispheres, responsible for the work of mimic muscles;
- nuclei located between the bridge and the medulla oblongata;
- lymph nodes and a grid of capillaries feeding nerve cells.

Functions
Anatomy of the facial nerve (the scheme is placed above) is considered. Now let's talk about its functions.
The main task of the facial nerve is to providemotor functions of the face. However, everything is complicated by the fact that before its branching into small parts it intertwines with the intervening nerve and partially shares its responsibilities with it. Through the internal auditory opening they move into the tunnel of the facial nerve, where a knee is formed from it, which provides the sensory to the intermediate nerve.
The facial nerve is the basis of the motor activity of almost all facial muscles, but in combination with the intervening nerve, it has taste and secretory fibers.
The pattern of the fibers of the facial nerve is very interesting and must be carefully considered.

Lesions of the facial nerve
In the event of a violation of the work orthere is paralysis of the motor muscles of the face. Visually, its asymmetry is observed: the relaxed part has a mask effect due to its immobility, the eye on the affected side does not close, lacrimation increases due to the fact that the mucosa irritates with dust and air, which in turn can cause conjunctivitis. Wrinkles on the forehead and the area around the nose and lips are straightened, the corners of the mouth pointing down, a person can not wrinkle his forehead.
The human face is often affected by the facial nerve (its branches, their anatomy and topography are detailed in the photo).

If, for some reason, the main one is affected,motor function, then we are talking about peripheral paralysis. It is characterized by the following external signs: paralysis of the muscles responsible for facial expressions, complete asymmetry of the face, the speech apparatus is broken, it is possible to take liquids only in a limited way. If the nerve was struck while it was located in the pyramidal bone, then in addition to the above signs, deafness and a lack of taste sensations are also noted.
Neuritis - characterized by inflammatoryneurological disease. It can manifest itself on the central part of the face and on the periphery. Symptoms depend on the area of the affected nerve. The disease develops either because of hypothermia (primary neuritis) or as a complication of other diseases (secondary).
It is characterized by a sharp onset, pain is given forear, asymmetry of the face is observed after a few days. Depending on the affected part, the symptoms may differ. With violations of the nucleus of the facial nerve, a person develops a muscle weakness of the face. When the nerve is infringed in the region of the bridge of the brain, strabismus arises, as well as paralysis of almost the entire musculature of the face. If the infringement occurred at the exit, the consequence of it will be a violation or short-term loss of hearing. Important is the facial nerve of a person. The structure, functions and problems have been studied for a long time.
With chronic otitis, neuritis may occurconcomitant nature, arising from inflammation in the middle ear, therefore can be accompanied by a sensation of lumbago. If there is parotitis, then there are symptoms of general intoxication - chills, body aches, high fever.

Principles of therapy
The scheme of treatment of the facial nerve for infringements and inflammatory processes must necessarily have a complex character. Therapy includes:
- diuretics, which remove liquid from the capillary network;
- glucocorticosteroid agents;
- drugs that dilate blood vessels;
- vitamins (usually group B).
This treatment eliminates the underlying causedisease, because the inflammation of the facial nerve is often the result of another disease, a secondary disease. Nervous ailments are often accompanied by very unpleasant sensations, so the patient is prescribed analgesic drugs. For treatment to be more rapid and effective, facial muscles need to provide complete peace.
The complex treatment also includesphysiotherapeutic procedures. Since the second week of the disease, it is allowed to apply facial massage and exercise physiotherapy exercises with gradually increasing load. Surgery is very rarely required. Surgical treatment is indicated when neuralgia is congenital or arising after a mechanical trauma. An operation of this kind is that wrongly fused and broken nerve endings are sewn together. Also, surgical intervention is justified when the drug treatment is ineffective for six months (maximum - eight months). If you ignore the process and do not use the listed methods of therapy, facial muscles can completely atrophy without the possibility of recovery in the future. The only way out is surgical facial plastic, the material for which is taken from the victim's leg.
Conclusion
Thus, with timely application formedical care and competent treatment, recovery and recovery will be quite long, but the outlook remains favorable. To avoid relapse, you need to monitor your health, avoid hypothermia and promptly treat inflammatory processes such as tonsillitis, acute respiratory infections, and so on.
We examined the facial nerve - anatomy and symptoms of damage, also describes the principles of treatment.
</ p>




