Toxoplasmosis in a cat - diagnosis, treatment

How do cats become infected with toxoplasmosis?
Pathogens of toxoplasmosis (parasites) - Toxoplasmagondii. They usually enter the cat's body after eating raw meat (goat, lamb, pork) and caught mice. Already in the first two weeks of the pathogen can be found in the feces of a cat.
Toxoplasma can be brought by man and from outside- on clothes, shoes. This means that the animal can get infected without even leaving the apartment. Between people transmission of the disease is possible only in the utero (mother-fetus).
Now - more about the life cycle andparasitic activity of toxoplasma. Having introduced into the cat's body, a part of toxoplasm is retained in the intestine and forms so-called cysts. Parasites begin to multiply inside cells. The cell, affected by Toxoplasma gondii, is dying. Cysts go outside with feces and become a source of infection already for other animals and humans.
The infection can only be prevented by cleaningfeces (immediately after defecation) and disinfection. After 3 weeks, the isolation of cysts into the external environment almost ceases. It turns out that the source of infection is an animal that has recently fallen ill.
The remaining part of toxoplasm, passing through the wallsintestine, advances to the spleen and bone marrow (the organs of hematopoiesis). Once in the blood, the parasite spreads through the body, affecting the cells of all organs. The defenses of the body in most cases inhibit (and sometimes block at all) the progress of toxoplasm by blood. The latter, thus trapped in the body, "wait for their time," not showing themselves in any way. That is why toxoplasmosis in a cat can not be determined, so to speak, "by sight".

Especially dangerous toxoplasm for the fetus,developing in the womb of an infected mother. The result of infection can be fetal death or miscarriage, multiple pathologies that are not amenable to treatment. If toxoplasmosis in a cat is found long before mating (ie, the cat has already had it), parasites can no longer damage the fetus, because they can not get to it through the placenta ("locked" by the body without the ability to move).
The most commonly diagnosed toxoplasmosis is ycats young (up to a year) and more mature (after 7 years), as well as those who eat raw meat (mice, birds, shop meat). Less resistant and weakened animals (sick, after childbirth, after suffering injuries).
Cold or all the same toxoplasmosis?
To symptoms of toxoplasmosis can be attributed to the lungcold and short-term disruption of the gastrointestinal tract. Usually such symptoms in a day or two come to naught. The disease, quickly passing into a latent form, is not clinically apparent (even with repeated infection), since specific antibodies have already been developed in the carrier's blood. Acute and subacute form are similar: lethargy, purulent discharge from the eyes and nose, a gastrointestinal disorder, often a rise in temperature. The respiratory system can also be affected (manifested in coughing, shortness of breath, wheezing, sneezing). All these symptoms can be attributed to a viral infection, so the diagnosis is not always correct.
When the nervous system is damaged,seizures, twitches and even paralysis. In this case, the death of the brain cells (both the head and spinal cord) is not ruled out, the field of which the nervous system can no longer fully work.

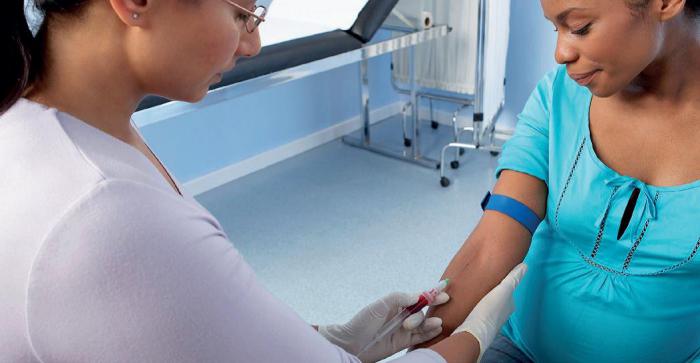
Since the first days of cysts with feces are notare allocated, diagnosis of the disease in these pores is almost impossible (or ineffective). The diagnosis is confirmed by a serological analysis of toxoplasmosis in cats (blood serum study). The vet may suggest taking an additional test (smear) from the nose (or pharynx).
Conventional preparations of antiparasitic propertieshere are powerless. Treatment is prescribed only by a veterinarian. That is why the article will not give recommendations on treatment. Your task is to follow the doctor's appointments and ensure that the sick cat is isolated from other animals and children until cysts cease to release into the environment.
Toxoplasmosis in a cat can be treated with difficulty,because the cells are inaccessible to drugs. Treatment is directed mainly at stopping the reproduction of Toxoplasma gondii and eliminating the symptoms of the disease. Improvements occur quite quickly (in a day, sometimes - two), but the course should be kept to the end.
</ p>