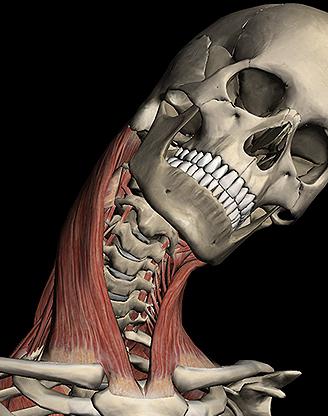
Breast-clavicular joint: structure
The sternoclavicular joint is not always clearly visible. Usually it occurs in people who are underweight or asthenic. If there is a small amount of subcutaneous fat tissue, it can be considered. In people with normal or increased body weight, it is visually indistinguishable. When palpation focus on the clavicle bones, between which, at the junction with the breastbone, below the cervical fossa, there are two symmetrical sternoclavicular joints.
Definition and location of the joint
Breast-clavicular joint - This is the place where the clavicle is joined to the sternum. It has an asymmetrical shape that compensates for the difference in size and shape of the bone notch and collarbone, allowing them to perfectly match each other. Inside the joint is an articular disc that compensates for the pressure between the bones, being a connecting element. Above, the entire joint is covered with a cartilaginous tissue that protects it from external influences and damages.
Breast-clavicular joint. Characteristic
The purpose of the joint is to connect the upper extremities with the thorax by combining the bones of the clavicle and the shoulder girdle with the trunk. In its origin, the sternoclavicular joint - It is a rudiment that is a compoundupper or forelimbs not only in humans, but also in animals since reptiles. He is very strong and participates in the movement of hands, the Reformation. This is particularly well felt when you raise your hands up and down. This connection allows the clavicle to move along the three major axes, synchronizing with the shoulder joint, supported by a powerful and very strong ligament apparatus.
Structure
Breast-and-clavicular joint in form resemblessaddle joint. In its structure it has a communicating form, having concavities and convexes corresponding to each other. This joint, having two axes and freely moving along them, from the point of view of simple mechanics is a universal joint. Its structure includes such cartilaginous tissues:
- cartilage covering of the clavicle;
- cartilage covering of the sternocostal cavity;
- a cartilaginous disk;
- cartilaginous tissue covering the joint.

Thus, the structure of the joint includes:
- the medial end of the clavicle with its main surface;
- upper ligament;
- ligament front;
- ribs-clavicular ligament;
- posterior ligament;
- concave arcs of the sternal-costal surface.
The sternoclavicular joint is also supported by:
- The intervertebral ligamentStretching over the notch of the jugular cavity of the sternum between the extremities of the clavicle bones.
- Complex of sternocleid ligament. By their location, they converge on the front, back and top surfaces of the joint, strengthening its strength.
- The most powerful and strong ligament in the sternum is the costal-clavicular. It passes from the uppermost edge of the first rib and rises to the collarbone. Controls the maximum uplift of the clavicle.

The thoracic-clavicular joint, in shape having a saddle structure, resembles spherical in its movement.
Damage
Due to its superficial location androle in the movements between the bones and joints of the shoulder girdle and trunk, the collarbone itself and the joints attached to it are often subjected to fractures and dislocations. Dislocation occurs as a result of sudden movements of the shoulder girdle posteriorly or downward and posteriorly. In this case, the anterior ligament is torn, forming a subluxation. With a stronger impact on this articulation, all ligaments are broken, releasing the clavicle from the joint fossa, forming a dislocation of this joint, which is easily recognized by external signs. Another type of dislocation occurs if the impact on the collarbone and the joint is direct, that is, by direct impact or strong pressure, when the posterior ligament is ruptured. Such a dislocation occurs inside the chest. It also occurs when the joint is exposed by strongly compressing the shoulders forward and inward. As a rule, with such influences, a fracture of the first or first four ribs of the sternum is observed.
Diseases
For this joint is characterized by such diseases,as ankylosis, which is a consequence of gonococcal or rheumatoid arthritis. After the age of forty, a disease with arthrosis often occurs, which during its course forms marginal osteophytes on the head of the clavicle. Soreness caused by exposure to the sternoclavicular joint, crunching, puffiness should be the reason for a visit to an osteopathic doctor.
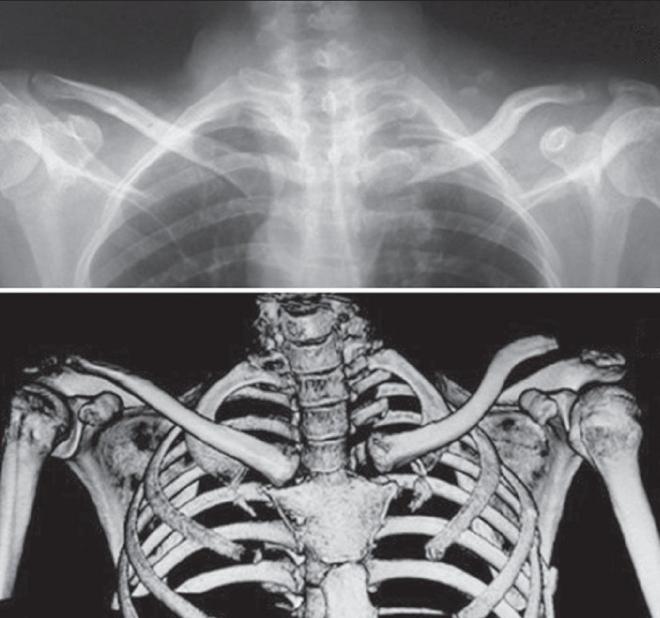
Aseptic necrosis attached to the sternumthe end of the collarbone, which is better known as Friedrich's syndrome, is determined even during palpation. Causes a painful swelling of the tissues around the joint, edemas and redness of the skin. Hyperostatic changes of the attached end of the clavicle are evident in marble disease (Paget's disease). The manifestation of hyperostosis is typical of congenital syphilis.
Diagnosis of changes in the joint
Methods for diagnosing diseases and disordersin the sternoclavicular joint are examination and palpation, an x-ray of the bones of the thorax. All studies are conducted by a traumatologist or an osteopath. The presence of any asymmetry or deformation, redness or pain when moving in the sternoclavicular junction, the appearance of a crunch in motion indicate the presence of one of the above diseases or injuries.

Palpation is performed by the second and third fingersright hand, while the doctor is located at the back or side of the patient. Fingers are installed in the middle of the sternum and orientated on the recess under the patient's neck, groping for the joint. For better detection, his patient is asked to raise his hands in a horizontal plane, which greatly facilitates the search.
Breast-clavicular joint in structure issimple. But while it is quite strong, it keeps the limbs attached to the body. If this joint is damaged, the arms become very limited and bring pain.
</ p>