Hernia in newborns: types, symptoms, treatment
Unfavorable environmental factors,intrauterine infections and hereditary predisposition all affect the formation of the connective and muscular tissue of the fetus. In connection with the disruption of their development, a manifestation of such a pathological condition as a hernia in newborn children is possible.
Such formations are a common pathology of infantile age, in which in some cases there is a need for surgical intervention.

The most common inguinal and umbilical formations, in adults the same often occurs in the hernia of the lumbosacral spine.
Statistics show a significant number of such diseases in newborns:
- inguinal hernia affects about 5% of children, most of it is for premature babies and males;
- umbilical kinds of this disease appear in every fifth child of infancy and every third with prematurity.
Such hernias disappear in 80% of cases as the umbilical ring grows. The decision on surgical intervention is made only in complicated cases.
Inguinal hernia is an indication for surgical treatment. In themselves they are not cured.
Umbilical hernia in newborns, photo
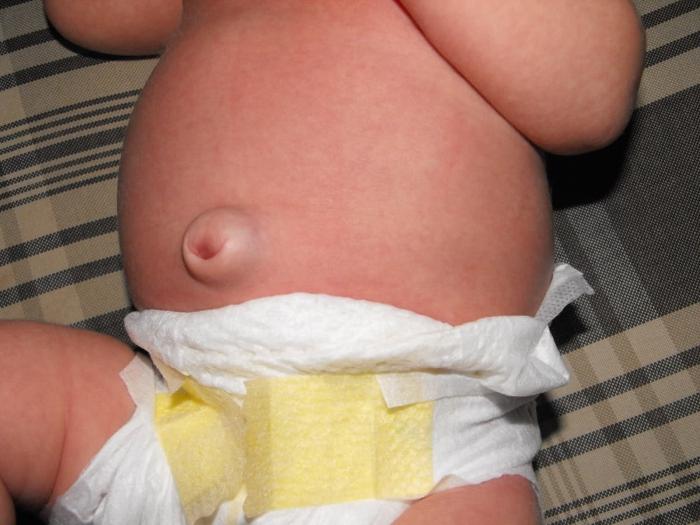
The main symptoms of this disease are:
- protrusion in the navel, manifested by crying and any other tension of the abdominal wall;
- an uncomplicated variant of painful sensations does not cause or limit the mobility of the infant.
A possible complication is a large increase insize and infringement of hernia formation. In this case, the child becomes extremely restless, experiencing discomfort and pain. In the navel area, a discoloration of the skin is observed, and hernial protrusion is strained and does not self-adjust. It becomes necessary to urgently consult a doctor and emergency surgical intervention.

The main goal of conservative treatment is the prompt closure of an existing defect - narrowing and overgrowing of the umbilical ring.
The following measures are carried out for medical purposes:
- General and professional massage of the abdominal wall, which is carried out by specialists.
- Physiotherapy exercises under the supervision of a physician.
- At home, before each feeding, you should lay the baby on the stomach (up to 10 minutes), and after doing the stroking of the abdomen along the clockwise direction.
- Sometimes the use of a firming patch is prescribed, but not more than a week.
Inguinal hernia in newborns children is a consequence of non-overgrowththe vaginal process of the peritoneum. On it in the uterine period the testicle moves from the abdominal cavity to the scrotum. Then the course must grow. If, for some reason, this does not happen, the part of the intestine may fall into the inguinal canal or scrotum. A hernial formation is formed with visual protuberance in the groin area.
This hernia must necessarily be treated surgically. It does not pass by itself and can lead to serious complications.
</ p>



