The thyroid gland is that of an organ? Functions and diseases of the thyroid gland
Thyroid belongs to that categoryorgans that exert a significant influence on the state of the whole organism. Therefore, any disease is fraught with serious consequences, and in the case of neglect of treatment, even a disability or more fatal outcome. Given this fact, it is worth exploring possible functional disorders of the thyroid gland.
What is the thyroid gland?
This important organ is the gland of the innersecretion. As its main function, it is possible to determine the production of hormones that make it possible to maintain the homeostasis stably. Without this, the full work of the whole organism as a whole is not possible.
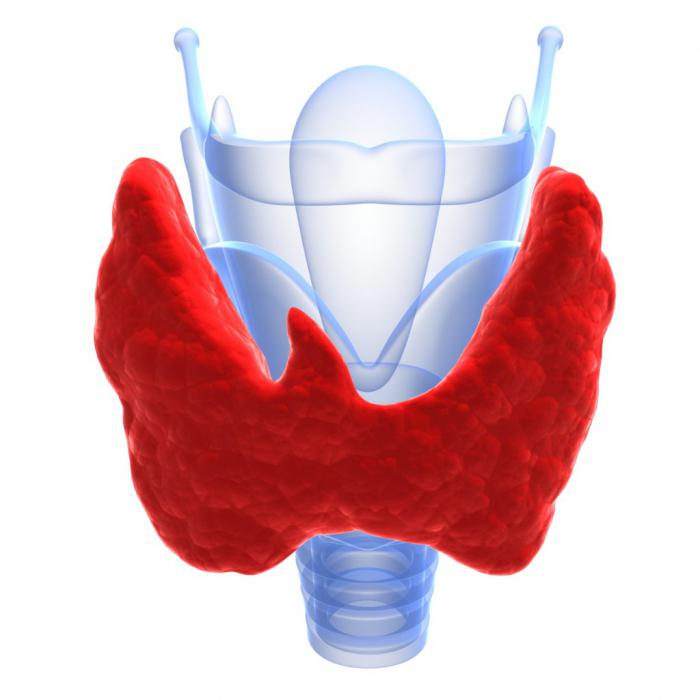
There is a thyroid gland in the anteriorthe triangle of the neck, bounded from above by the base of the lower jaw, from below - by the jugular cutting of the sternum, and on the sides by the front edges of the right and left sternocleidomastoid muscles. As the person grows up, the location of this organ may change somewhat. For example, if the children of iron are fixed at the level of the thyroid cartilage, then in people aged it is lowered significantly lower (it is in this position that this organ forms the so-called sternum).
Parameters and composition
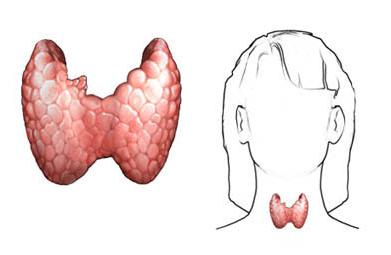
The thyroid gland is an organ in whichincludes two lobes and an isthmus. Directly the crescents themselves are on the front surface of the trachea. But the shares are adjacent to it from the left and right side. In some cases it is also possible to have an additional share, which has a pyramidal shape.
It should be noted that the thyroid gland isThe largest element of the endocrine system. At the same time, its right lobe is larger than the left one and is characterized by abundant vascularization. If we talk about the mass of the thyroid gland, then, as a rule, it is in the range of 20 to 60 grams. And this indicator increases during puberty and decreases with the onset of old age.
Interesting is the fact that the thyroidiron in women is less than in men, although during pregnancy it becomes larger. Also for this organ, which is one of the most blood supply, is characterized by the presence of an external and internal connective capsule. It is the outer capsule that performs a key function in the formation of the ligamentous apparatus necessary to fix the gland on the trachea and larynx.
The process of blood supply
The thyroid gland is the organ for whicha significant amount of blood is needed. It is for this reason that it has an extensive venous and developed arterial system. If we compare the intensity of blood flow of various parts of the body, then in the thyroid gland it will be 50 times stronger than in muscle fibers. This indicator can significantly increase in the case of diseases that are accompanied by increased release of hormones.
Submission of blood to the thyroid gland is carried outthrough the two upper and lower thyroid arteries, which form an anastomosis with each other. The outflow of blood and lymph is due to the active work of the venous and lymphatic systems. In the case of pathological conditions from the thyroid gland, thyroid-stimulating and thyreblocking immunoglobulins, as well as antithyroid antibodies, are excreted.
Innervation of the thyroid gland is made possible by twigs of the vagus nerve and branches of the cervical ganglia.
Functions of hormones
It is worth recalling that the thyroid gland isan element of the endocrine system. So, it makes sense to talk about the production of hormones. This body secretes three types of substances: calcitonin (peptide hormone) and two iodine-containing elements - thyroxine and triiodothyronine. Synthesize the latter helps the apical part of the thyroid epithelium, as well as the intrafollicular space (has a partial effect). Calcitonin production is due to the thymus and parathyroid gland, with the active promotion of C-cells. Without it, it would not be possible to regulate potassium and phosphorus metabolism in the human body.
In fact, the thyroid hormone is a substance for which biological activity is characteristic. In the process of this activity, it exerts a remote effect on various cells of the body.
Thyroid hormones, for example, are necessary forsuccessful synthesis of proteins in organs and tissues. A reserve for them is thyreoglobulin. But the main goal of thyroid hormones is to provide chemical reactions that play a key role in the energy production process that the body needs to function properly, even at rest.
The thyroid hormone is an element without which the proper operation of the heart, intestinal peristalsis and stable maintenance of the desired body temperature become impossible.
Dysfunction in the thyroid gland
Hormones have a significant effect on the entire body, maintaining basic metabolism at the right level. Therefore, in the case of their excess, this exchange is accelerated, and in the case of a deficit, it slows down.
All possible pathologies of the thyroid gland can be divided into several main types:
- diseases accompanied by a decrease in the level of hormones - hypothyroidism;
- pathologies in which the synthesis of hormones increases (thyrotoxicosis);
- diseases that occur without changes in the functional activity of the gland, but stimulate morphological changes in its structure (hyperplasia, goiter, formation of nodes, etc.).
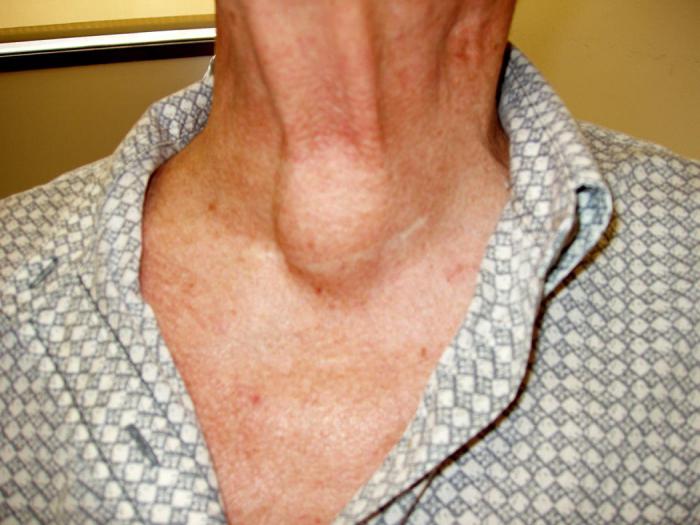
One of the main reasons for the emergence ofpathological conditions is a lack of iodine in the body. Therefore, it is always important to monitor food, because there are foods that enrich the cells with this useful element, as well as interfere with its penetration into the tissues of the thyroid gland.
Common diseases
To begin, perhaps, it is necessary with such diagnosis, asa node of the thyroid gland. This disease has complicated the lives of many people. In fact, the thyroid gland is a small part of its tissue, which is surrounded by a capsule. Such a change is caused by a lack of iodine, as a result of which the gland begins to work more intensively, absorbing this element from the blood. The emerging goiter expands the vessels, while sealing the tissues. The result of this process is the formation of a node. Focal changes in the thyroid gland are another name for this pathology.
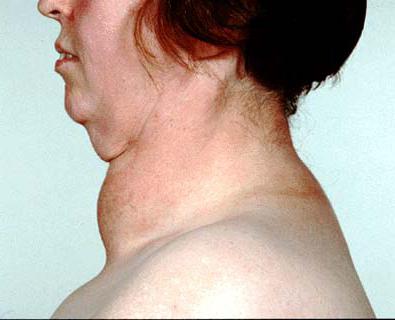
Physicians are increasingly faced with the emergence ofseveral seals simultaneously, the danger of which lies in the fact that they can develop from benign to malignant. If such changes have occurred, it is necessary to do the operation. A benign surgical site does not require and is treated by enriching the body with iodine.
Vascularization of the thyroid gland is anothera problem that is closely related to the formation of nodes. Its essence boils down to the fact that in addition to the four arteries, new blood vessels are formed in the gland, the appearance of which is caused by seals (nodes). The fact that vascularization is increased can be learned from the following symptoms:
- painful muscular sensations;
- frequent occurrence of a goitre sensation;
- changes in blood pressure;
- rapid change in weight;
sweating;
- edema formation;
- hormonal disorders;
- increased drowsiness and fatigue.
In addition to these manifestations of increased blood flow inthe area of the thyroid gland, attention and memory, and sometimes even the sexual function, can be reduced. To treat such a pathology, it is necessary to consult an endocrinologist.
Function malfunctioning
From the normal functioning of the thyroid gland depends both the integrity of the immune system itself and the work of the organism as a whole. Therefore, any failure is fraught with tangible consequences.
The lowered function of the thyroid gland is weakening of the work of this body. This problem has another name - hypofunction. There are several reasons why functional activity may decrease:
- diseases caused by the inflammation of the gland or its injury;
- congenital anomalies;
- lack of iodine in the body;
- extremely unfavorable environmental factors that led to damage to the thyroid gland.
As for secondary hypofunction, in this case, it is worth paying attention to the damage to the pituitary gland, which regulates the gland.
Thyroid hypothyroidism is anothera problem that can not be ignored. The bottom line is that the speed of hormone production depends on the full-fledged work of all body systems and the ability to cope with constant stresses. If the functions of the thyroid gland slow down, then this will give rise to a chain reaction, which will significantly aggravate the general condition of the person. And if before there were other health problems, then overcoming them will become much more difficult.
The most common method of treatment fora similar diagnosis is hormone replacement therapy. Sometimes, in order to restore the functionality of the gland back to normal, it is enough to take thyroid hormones for several months.
Another problem worthy of attention is the hyperfunction of the thyroid gland. This is a syndrome that develops due to an increase in the production of hormones such as triiodothyronine and thyroxine.
This disease can be divided into three types: primary, secondary and tertiary hyperthyroidism. In most cases, the background for the development of such a problem is diffuse toxic goiter. It is this type of compaction of the gland tissues that can be attributed to the factor provoking excessive production of hormones.
Hyperfunction of the thyroid gland is a disease that can develop due tosubacute thyroiditis, viral lesion of the gland, nodular goiter or toxic adenoma. The consequences of such an unpleasant diagnosis are severe nervousness, memory impairment, ophthalmopathy (eyelash), accompanied by an increase in the thyroid gland, insomnia and poisoning of the body with excess hormones.
In general, there is an excessive strain of allsystems and organs leading to irreversible changes. As a result, a person can become disabled and even die. Treat hyperthyroidism through drugs that reduce the production of hormones, through surgical intervention and with the help of radioactive iodine.
Other common pathologies
Often, the townsfolk have to facesuch a serious diagnosis as hyperplasia of the thyroid gland. This is nothing more than an increase in the functional cells of this organ. As a result, the size of the thyroid gland is markedly increased. This is known to many so-called goiter.
The cause of this disease can bebe both excessive and inadequate production of hormones. But in general, such a syndrome is able to develop on the basis of absolutely different diseases. And depending on the cause, the treatment strategy also changes. The proliferation of functional cells has several types:
- nodal (enlargement of the gland due to the appearance of cysts and nodes);
- diffuse (uniform increase without formation of consolidations);
- mixed.
To determine the fact that the syndrome developsincrease of thyroid cells, it is possible by such signs as rapid weight change, the appearance of swelling in the neck, excessive constant excitability, restless sleep and nervousness. These symptoms will help to know the onset of hyperplasia and quickly take appropriate measures.
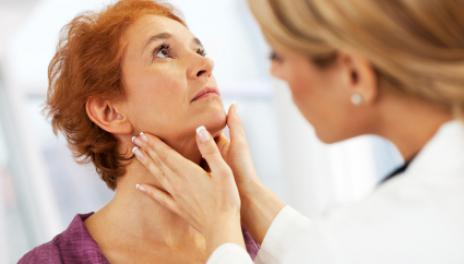
Another pathology, which often has to be treated by endocrinologists, is hypoplasia of the thyroid gland. it congenital malformation of the development, which is manifested ininsufficient development of the tissue of this organ. The reason that people have to face such a diagnosis is the lack of iodine in the body of a woman during pregnancy. Different defects of intrauterine development can also play a negative role when the function of the thyroid gland decreases during the period of gestation. This disease can be detected already in childhood, because it is the cause of hypothyroidism and cretinism.
The key method for overcoming hypoplasia isuse of thyroid hormones. And with the treatment of delay is not worth it. Also, you will have to provide the child with massage sessions and therapeutic gymnastics. This is important for the reason that in most cases, children with a similar disease develop a violation of muscle tone and movements.
It is not uncommon for patients to come toendocrinologists with a problem such as a heterogeneous thyroid gland. What this is, will best explain the terminology of ultrasound therapy, according to which a similar problem is called diffuse change. It is about changing the tissues of the thyroid gland, in which the entire organ reflects the sound incorrectly.
The reasons for this change can beseveral, the main - a permanent lack of iodine in the body. The unevenness of the thyroid gland tissues also develops on the basis of the following diseases: subacute thyroiditis, endemic goiter, chronic autoimmune thyroiditis, diffuse toxic and mixed goiter. As a rule, tissue inflammation occurs due to pathological aggression of the body's immune system.
Speaking about treatment, it is worth noting that anyimprovisation is fraught with negative consequences, so it is necessary to initially visit a qualified doctor. In most cases, specialists prescribe to patients products containing iodine or potassium iodide. But in case of detection of thyroid dysfunctions, a synthetic analogue of the thyroid hormone is prescribed. In the event that expanding tissues begin to exert pressure on neighboring organs, it is worth seriously thinking about surgical intervention.
It is also important to know about such a problem asincreased echogenicity of the thyroid gland. What is it, you can understand only if you use ultrasound. The bottom line is that this term is used only to describe the pattern of ultrasound. This word characterizes the ability of a tissue to reflect the sound of a high frequency directed at it.
The very fact of changing the pattern of ultrasoundresearch indicates the appearance of any pathology. In any case, the ultrasound technique helps to more accurately diagnose a disorder in the state or functions of the thyroid gland.
Autoimmune thyroiditis
This problem deserves special attention. It is important to understand, faced with such a diagnosis as "thyroid gland AIT," that this is a fairly serious disease requiring a thorough approach to the treatment process. The essence of this problem is that the organ has a chronic inflammation of the tissues, which has an autoimmune origin. The reason for the development of such a state is the negative impact of the body's immune system on the cells of the thyroid gland.

It is worth noting that such a diagnosis isup to 30% of all diseases associated with the gland. In this case, this problem occurs in women 15-20 times more often than men. At risk are people aged 40 to 50 years.
Autoimmune thyroiditis can be divided into several types:
- Bezboleff. Develops with a significant decrease in immunity and is thus idiopathic in nature.
- Cytokine-induced. This form of the disease manifests itself after the use of interferon, which is used to treat liver and blood diseases.
- Chronic. The cause of this type of thyroiditis is an increase in the number of antibodies and T-lymphocytes in the tissues of the gland.
- Postpartum. The disease develops as a result of pregnancy.
Of course, understanding the issue of "thyroidiron AIT - what is it? ", it is worth paying attention to the treatment. Hearing this diagnosis, first of all you need to go to the doctor. In most cases, after the diagnosis, patients are prescribed hormone replacement therapy. Take prescribed drugs every day with a constant increase in the dose.
If the disease is in a neglected stage, andgoiter has reached a considerable size, it will be necessary to turn to the help of surgeons, since it is unlikely to achieve tangible progress in treatment without surgical intervention.
It is important not to resort to inflammation during the inflammationto the use of antibiotics. This does not help neutralize the effect of the virus, and the pathology will continue to progress. We need to focus on competent and timely therapy under the guidance of a specialist. This approach is able to give the desired result.
Importance of prevention
Based on the above information can be doneconclusion that the affected thyroid gland is dangerous. Therefore, for any suspicious symptoms, it is necessary to go to the examination and in case of revealing the pathological condition of the organ without delay begin treatment. In order to reduce the risk of thyroid diseases to a minimum, you need to follow a few simple rules: enrich your diet with foods high in iodine, constantly sanitize the mouth (often through teeth affected by caries, the infection penetrates into the gland) and thoroughly approach the treatment of any catarrhal diseases.
With competent and thorough prevention, many difficulties associated with thyroid diseases can be avoided.
</ p>