As a result of mitosis, new cells are formed: the features and significance of the process
One of the points of the well-known theory of cellularstructure is the statement about the appearance of new cells from the original, that is, the mother. But this can happen in two ways. One of them is mitosis. It is essential for the process of reproducing oneself. What cells are formed as a result of mitosis, what is their number and the features of the process - all this will be discussed in detail in our article.
Cell cycle
A cell of any organism can exist inthe interval between its two crushes or from the beginning of this process to the moment of death. This stage of time is a cell cycle. It includes the stages of the process of division and a certain time interval between them, which is called the interphase. During this period, the cells grow and the formation of nutrients.

But one of the most important moments is the process of doubling DNA macromolecules. There all the genetic information about the cell is encrypted.
How cells are divided
With the help of meiosis, spermatozoa multiply andeggs. The essence of this process is the formation of four haploid gametes from the mother cell with a double set of chromosomes. For this reason it is also called reduction division. This is very important, because when fertilization from the sex cells there is a new organism containing half the hereditary information from the mother and father. And this becomes possible only if the gametes are haploid.

What cells are formed as a result of mitosis? The answer is simple: diploid, that is, with a double chromosome set. This process is also important. The thing is that as a result of mitosis cells are formed, which are an exact copy of the mother. All of them are somatic.
Phases of mitosis
The process of formation of new somatic cells includes several phases. Their total duration, depending on the type of organism, ranges from a couple of minutes to several hours.
The initial stage is called prophase. At this time, the chromatin filaments are condensed, the nucleoli decrease, and the spindle is fissioned. The shell of the nucleus disintegrates, because of the chromosome they enter the cytoplasm.
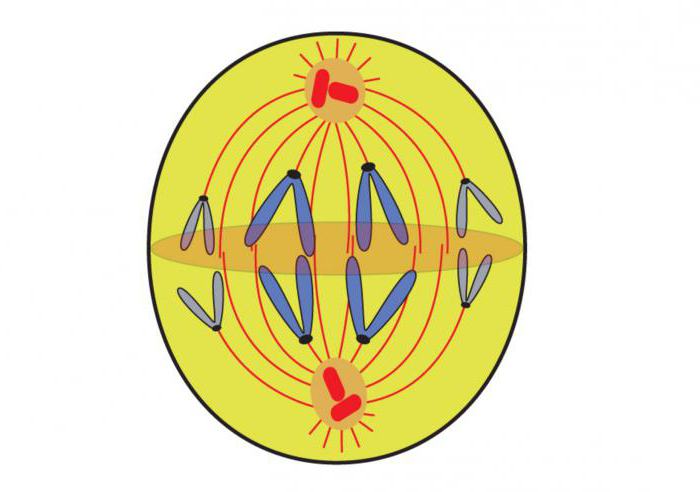
The second stage is called metaphase. Its essence lies in the construction of chromosomes in one plane and the attachment to them of the filament spindle threads. Next is anaphase, which is the shortest stage. As a result of mitosis, fully formed daughter cells are formed. This process is completed at the telophase stage. In this case, the chromosomes are despiralized. They are almost invisible under a light microscope. Next, the shell of the nucleus begins to form around the chromatid, and the fission spindle gradually disappears.
How many cells are formed as a result of mitosis
Mitosis as a method of dividing eukaryotic cellsis the most common in nature. Recovery of lost or damaged parts of the body is due to this process. As a result of mitosis, two daughter cells from one maternal body are formed. At the same time, due to the doubling of the DNA molecule in the interphase of the cell cycle, the diploid chromosome set is preserved.

Mitosis is the basis of all kinds of asexual reproduction: vegetative - in plants, dividing the cells in two - in the simplest, multiple crushing - in malarial plasmodium, sporulation - in fungi and fern-like, budding - in coelenterates.
Biological significance of mitosis
As a result of mitosis, cells with the samechromosome set, as the mother. As a result, the process of transferring genetic information is ensured, no matter how many constant divisions occur. During this process, the number of chromosomes and the sequence of nucleotides in DNA molecules remain constant.
Thus, as a result of mitosis from onecells form two children, which completely copy the original. This ensures the stability of karyotypes and is an indispensable condition for the existence of all living organisms throughout the entire period of their individual and historical development.
</ p>



